
Second Academic Year for Medication Safety Scholars Program
March 22, 2024
Really excited to share the news that we will be beginning the second academic year for the Emily Jerry Foundation‘s Medication Safety Scholars Program! This comprehensive distance education and virtual engagement program was developed and successfully implemented over the… Read More




Indiana Scorecard
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
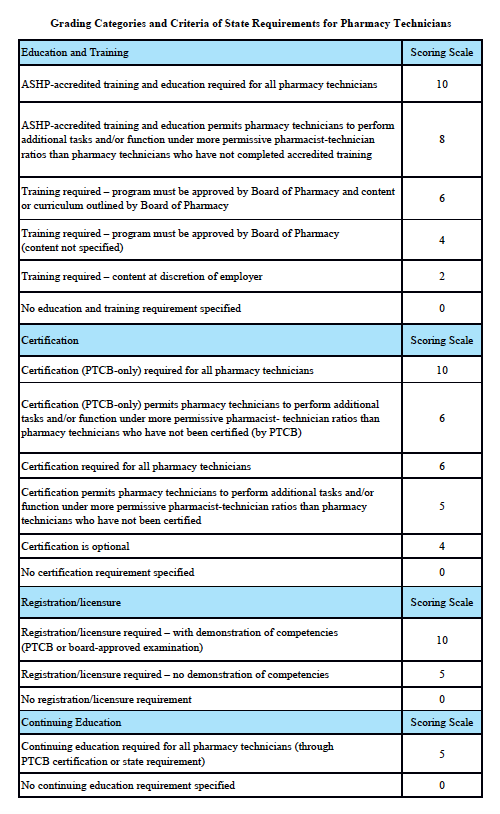
Indiana Law
I. Laws
Chapter 19
IC 25-26-19 Chapter 19. Regulation of Pharmacy Technicians
IC 25-26-19-1 “Board”
Sec. 1. As used in this chapter, “board” refers to the Indiana board of pharmacy established by IC 25-26-13-3. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3
IC 25-26-19-2 “Pharmacy technician”
Sec. 2. As used in this chapter, “pharmacy technician” means an individual who:
(1) works under the direct supervision of a pharmacist licensed under this article; and
(2) performs duties to assist a pharmacist in activities that do not require the professional judgment of a pharmacist. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-3 “Pharmacy technician in training”
Sec. 3. As used in this chapter, “pharmacy technician in training” means a person who is enrolled in a training program for pharmacy technicians prescribed by the board. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-4 Adoption of rules
Sec. 4.
(a) The board may adopt rules under IC 4-22-2 to:
(1) implement and enforce this chapter;
(2) set fees under IC 25-1-8; and
(3) establish education and training requirements for certification to practice as a pharmacy technician.
(b) The board shall:
(1) establish standards for the competent practice of pharmacy technicians; and
(2) subject to IC 4-21.5, IC 25-1-7, and IC 25-1-9, conduct proceedings on any matter under the jurisdiction of the board. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-5 Qualification for pharmacy technician certificate
Sec. 5. (a) The board shall issue a pharmacy technician certificate license to an individual who:
(1) applies to the board in the form and manner prescribed by the board;
(B) completed an employer provided training program that:
(i) beginning July 1, 2015, uses training requirements and minimum standards developed by the board; (ii) has been approved by the board; and
(iii) includes specific training in the duties required to assist the pharmacist in the technical functions associated with the practice of pharmacy;
(C) successfully passed a certification examination offered by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board or another nationally recognized certification body approved by the board.
(2) is at least eighteen (18) years of age;
(3) has not been convicted of a crime that has a direct bearing upon the individual’s ability to practice competently;
(4) is not in violation of this chapter or rules adopted by the board under section 4 of this chapter;
(5) has paid the fee set by the board under section 4 of this chapter; and
(6) has completed a program of education and training approved by the board or has passed a certification examination offered by a nationally recognized certification body approved by the board. (b) For good cause, the board may waive the age requirement under subsection (a)(2). As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-6 Qualification for pharmacy technician in training permit
Sec. 6.
(a) The board shall issue a pharmacy technician in training permit to an individual who:
(1) applies to the board in the form and manner prescribed by the board;
(2) is at least eighteen (18) years of age;
(3) has not been convicted of a crime that has a direct bearing upon the individual’s ability to practice competently;
(4) is not in violation of this chapter or rules adopted by the board under section 4 of this chapter; and
(5) has applied for certification under section 5 of this chapter.
(b) An applicant:
(1) may work as a pharmacy technician in training without a permit for not more than thirty (30) consecutive days after the applicant files an application under this section;
(2) shall provide the applicant’s employer with a receipt issued by the board that: (A) provides the date an application under this section was filed; and (B) indicates that the fee has been paid; 239 before the applicant may begin work as a pharmacy technician in training; and
(3) may request an additional thirty (30) day period to practice as a pharmacy technician in training without a permit. The board may approve a request under this subdivision if the board determines that the extension is for good cause.
(c) A pharmacy technician in training permit expires on the earliest of the following:
(1) The date the permit holder is issued a pharmacy technician certificate under this chapter.
(2) The date the board disapproves the permit holder’s application for a pharmacy technician certificate under this chapter.
(3) The date the permit holder ceases to be enrolled in good standing in a pharmacy technician training program approved by the board. The graduation of a permit holder from a pharmacy technician program does not cause the permit to expire under this subdivision.
(4) Sixty (60) days after the date that the permit holder successfully completes a program approved by the board.
(5) Twelve (12) months after the date of issuance.
(d) For good cause, the board may waive the age requirement in subsection (a)(2). As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-7 Expiration of pharmacy technician certificate; renewal fee; reinstatement of pharmacy technician certificate
Sec. 7.
(a) A pharmacy technician certificate expires on a date set by the Indiana professional licensing agency in each even-numbered year.
(b) An application for renewal of a pharmacy technician certificate must be accompanied by the appropriate fee.
(c) If a person fails to renew a pharmacy technician certificate, the certificate may be reinstated by meeting the requirements under IC 25-1-8-6.
(d) The board may require a person who applies for a certificate under subsection (c) to appear before the board and explain the reason why the person failed to renew a pharmacy technician certificate. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3. Amended by P.L.1-2006, SEC.466.
IC 25-26-19-8 Prohibited activities of a certified pharmacy technician
Sec. 8. A certified pharmacy technician may not perform the following activities:
(1) Providing advice or consultation with the prescribing practitioner or other licensed health care provider regarding the patient or the interpretation and application of information contained in the prescription or drug order, medical record, or patient profile.
(2) Providing advice or consultation with the patient regarding the interpretation of the prescription or the application of information contained in the patient profile or medical record.
(3) Dispensing prescription drug information to the patient.
(4) Final check on all aspects of the completed prescription and assumption of the responsibility for the filled prescription, including the appropriateness of the drug for the patient and the accuracy of the:
(A) drug dispensed;
(B) strength of the drug dispensed; and
(C) labeling of the prescription.
(5) Receiving a new prescription drug order over the telephone or electronically unless the original information is recorded so a pharmacist may review the prescription drug order as transmitted.
(6) Any activity required by law to be performed only by a pharmacist.
(7) Any activity that requires the clinical judgment of a pharmacist and is prohibited by a rule adopted by the board. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-9 Specific violations
Sec. 9.
(a) An individual may not practice as a pharmacy technician unless the individual is certified under this chapter.
(b) An individual may not act as a pharmacy technician in training unless the individual has obtained a permit under this chapter or the individual is acting as a pharmacy technician in training during the period permitted under section 6(b) of this chapter.
(c) An individual who knowingly violates this section commits a Class D felony. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
IC 25-26-19-10 Injunctions
Sec. 10.
(a) If an individual violates this chapter, the attorney general, the board, or the prosecuting attorney of the county in which the individual violates this chapter may maintain an action in the name of the state to enjoin the individual from continued violation of this chapter.
(b) An injunction issued under this section does not relieve an individual person from criminal prosecution but is in addition to any remedy provided under criminal law. As added by P.L.251-2003, SEC.3.
II. Regulations
Rule 35 pharmacy technicians
Rule 35. Pharmacy Technicians
856 IAC 1-35-1 Purpose and scope
Authority: IC 25-26-13-4
Affected: IC 25-26-13
Sec. 1.
(a) The board is responsible for establishing standards for the competent practice of pharmacy.
(b) The use of pharmacy technicians to assist the pharmacist with nondiscretionary functions associated with the practice of pharmacy enables the pharmacist to provide pharmaceutical care to the patient.
(c) Evolved pharmacy practice demands additional time for pharmacists to counsel individual patients regarding the proper use of drugs.
(d) Only pharmacists (licensed under IC 25-26-13-11), pharmacy interns and externs (as defined in IC 25-26-13-2 and registered under IC 25-26-13-10), and pharmacy technicians as described in this section shall be permitted to participate in the activities associated with a drug order or prescription preparation.
(e) A pharmacist shall not permit a pharmacy technician to participate in the activities associated with a drug order or prescription preparation unless the pharmacy technician meets the qualifications of this section.
(f) The pharmacist is responsible for the work performed by the pharmacy technician under the pharmacist’s supervision.
(Indiana Board of Pharmacy; 856 IAC 1-35-1; filed Aug 17, 1995, 8:30 a.m.: 19 IR 39; readopted filed Nov 13, 2001, 3:55 p.m.: 25 IR 1330; filed Dec 20, 2002, 12:17 p.m.: 26 IR 1561; readopted filed Oct 4, 2007, 3:33 p.m.: 20071031-IR-856070060RFA)
856 IAC 1-35-2 “Unlicensed person” defined
Authority: IC 25-26-13-4
Affected: IC 25-26-13-18
Sec. 2.
(a) As used in this rule, “unlicensed person” means a pharmacy technician who, under the immediate and direct supervision of the pharmacist, assists the pharmacist in the technical and nonjudgmental functions related to the practice of pharmacy in the processing of prescriptions and drug orders.
(b) As used in subsection (a), “pharmacy technician” shall not include pharmacy intern/externs or other ancillary persons which include, but are not limited to:
(1) clerks;
(2) secretaries;
(3) cashiers; or
(4) delivery persons; who may be present in the pharmacy.
(Indiana Board of Pharmacy; 856 IAC 1-35-2; filed Aug 17, 1995, 8:30 a.m.: 19 IR 40; readopted filed Nov 13, 2001, 3:55 p.m.: 25 IR 1330; readopted filed Oct 4, 2007, 3:33 p.m.: 20071031-IR-856070060RFA)
856 IAC 1-35-3 “Pharmaceutical care” defined
Authority: IC 25-26-13-4
Affected: IC 25-26-13 77
Sec. 3. As used in this rule, “pharmaceutical care” means the responsible provision of drug therapy for the purpose of achieving definite outcomes that improve a patient’s quality of life.
(Indiana Board of Pharmacy; 856 IAC 1-35-3; filed Aug 17, 1995, 8:30 a.m.: 19 IR 40; readopted filed Nov 13, 2001, 3:55 p.m.: 25 IR 1330; readopted filed Oct 4, 2007, 3:33 p.m.: 20071031-IR-856070060RFA)
856 IAC 1-35-4 Qualifications
Authority: IC 25-26-13-4
Affected: IC 25-26-13-18
Sec. 4. To be eligible to perform the functions and duties of a pharmacy technician, an individual must possess the following qualifications, which shall be ascertained and documented in a reasonably retrievable manner by the pharmacist that qualifies the pharmacy permit:
(1) The individual has not been convicted of a crime that has a direct bearing on the individual’s ability to work with legend drugs or controlled substances.
(2) The individual must be a high school graduate or have successfully completed a General Education Development program or have been judged to be competent by the qualifying pharmacist.
(3) The individual must have successfully completed or be enrolled in and successfully complete within twelve (12) months of being hired as a technician one (1) of the following board-approved programs:
(A) A comprehensive curricular-based education and training program conducted by a pharmacy or educational organization.
(B) A technician training program utilized by the employer that includes specific training in the duties required to assist the pharmacist in the technical functions associated with the practice of pharmacy. The contents of the training program shall include, at a minimum, the following:
(i) Understanding of the duties and responsibilities of the technician and the pharmacist, including the standards of patient confidentiality and ethics governing pharmacy practice.
(ii) Tasks and technical skills, policies, and procedures related to the technician’s position.
(iii) Working knowledge of pharmaceutical-medical terminology, abbreviations, and symbols commonly used in prescriptions and drug orders.
(iv) Working knowledge of the general storage, packaging, and labeling requirements of drugs, prescriptions, or drug orders.
(v) Ability to perform the arithmetic calculations required for the usual dosage determinations.
(vi) Working knowledge and understanding of the essential functions related to drug purchasing and inventory control.
(vii) The record keeping functions associated with prescriptions or drug orders.
(4) In lieu of the requirements in subdivision (3), the successful completion of a board-approved certification examination may satisfy the requirements of this section.
(5) A record of the pharmacy technician training and education must be maintained in the pharmacy where the technician is employed and shall include the following:
(A) The name of the pharmacy technician.
(B) The starting date of employment as a pharmacy technician.
(C) The starting date of the technician training program.
(D) The date of completion of the training program or proof of passing the board-approved examination if subdivision (4) applies.
(E) A copy of the training manual, if on-the-job training is used by the employer, or certificate of successful completion of another approved program, or other training program completed prior to employment.
(Indiana Board of Pharmacy; 856 IAC 1-35-4; filed Aug 17, 1995, 8:30 a.m.: 19 IR 40; readopted filed Nov 13, 2001, 3:55 p.m.: 25 IR 1330; filed Dec 20, 2002, 12:17 p.m.: 26 IR 1562; readopted filed Oct 4, 2007, 3:33 p.m.: 20071031-IR-856070060RFA)
856 IAC 1-35-5 Duties that a pharmacy technician may not perform
Authority: IC 25-26-13-4
Affected: IC 25-26-13-18
Sec. 5. A pharmacy technician may perform many technical functions associated with the practice of pharmacy. However, even under the immediate and direct supervision of a pharmacist, the pharmacy technician is prohibited from performing the following functions:
(1) Any duty required by law, regulation, or rule to be performed by a pharmacist.
(2) The provision of advice or consultation with the prescriber or other licensed health care provider regarding the patient or the interpretation and application of information contained in the prescription or drug order, medical record, or patient profile.
(3) The provision of advice or consultation with the patient regarding the interpretation of the prescription or the application of information contained in the patient profile or medical record.
(4) Dispensing of prescription drug information to the patient as required in IC 25-26-13-4.
(5) Receipt of a verbal prescription, other than a refill approval or denial, from a prescriber.
(6) Final check on all aspects of the completed prescription and assumption of the responsibility for the filled prescription, including, but not limited to, accuracy of the:
(A) drug;
(B) strength; and
(C) labeling.
(Indiana Board of Pharmacy; 856 IAC 1-35-5; filed Aug 17, 1995, 8:30 a.m.: 19 IR 41; readopted filed Nov 13, 2001, 3:55 p.m.: 25 IR 1330; readopted filed Oct 4, 2007, 3:33 p.m.: 20071031-IR-856070060RFA) 78
856 IAC 1-35-6 Provision of quality assurance; duties (Repealed)
Sec. 6. (Repealed by Indiana Board of Pharmacy; filed Dec 20, 2002, 12:17 p.m.: 26 IR 1562)
856 IAC 1-35-7 Identification
Authority: IC 25-26-13-4
Affected: IC 25-26-13-18
Sec. 7.
(a) The public shall be able to identify a pharmacist from a pharmacy technician while engaged in the provision of pharmaceutical care.
(b) A pharmacy technician shall:
(1) wear identification clearly stating that the person is a pharmacy technician while on duty; and
(2) identify himself or herself verbally in any telephonic or electronic communication as a pharmacy technician.
(c) No person, other than a person who has met the qualifications established in section 4 of this rule, will be permitted to wear identification using the words “pharmacy technician” or similar wording that may confuse or deceive another person.
(Indiana Board of Pharmacy; 856 IAC 1-35-7; filed Aug 17, 1995, 8:30 a.m.: 19 IR 41; readopted filed Nov 13, 2001, 3:55 p.m.: 25 IR 1330; readopted filed Oct 4, 2007, 3:33 p.m.: 20071031-IR-856070060RFA)
References
Indiana code and administrative code
http://www.in.gov/pla/files/2011_BoP_and_PLA_Compilation(1).pdf
Senate Bill 233
http://iga.in.gov/legislative/2014/bills/senate/233/#
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives