
Second Academic Year for Medication Safety Scholars Program
March 22, 2024
Really excited to share the news that we will be beginning the second academic year for the Emily Jerry Foundation‘s Medication Safety Scholars Program! This comprehensive distance education and virtual engagement program was developed and successfully implemented over the… Read More



Idaho Scorecard
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
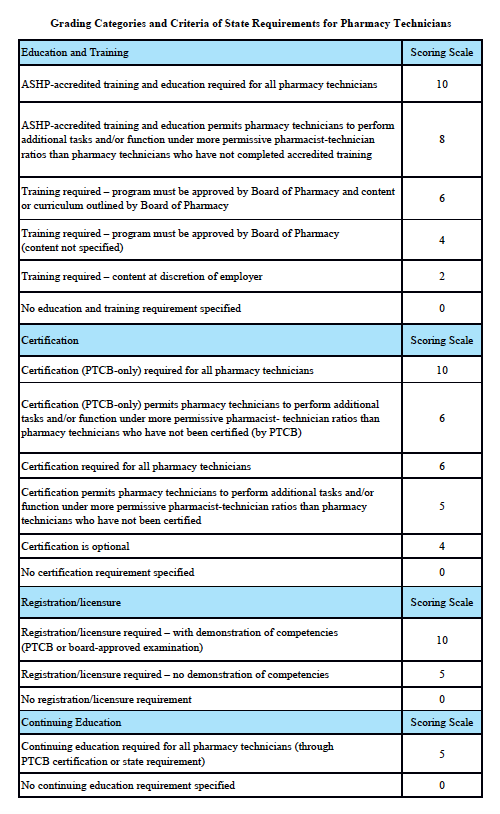
Idaho Law
I. Laws
No formal language regarding pharmacy technicians.
II. Regulations
012.DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS
040.CERTIFIED PHARMACY TECHNICIAN REGISTRATION.
041.TECHNICIAN-IN-TRAINING REGISTRATION.
410.VERIFICATION TECHNICIAN PROGRAM
012.DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS (S — Z).
01. Sample. A unit of a drug that is not intended to be sold and is intended to promote the sale of the drug. (3-21-12)
02. Secured Pharmacy. The area of a drug outlet where prescription drugs are prepared, compounded, distributed, dispensed, or stored. (3-21-12)
03. Skilled Nursing Facility. An institutional facility or a distinct part of an institutional facility that is primarily engaged in providing daily skilled nursing care and related services. (3-21-12)
04. Student Pharmacist. A term inclusive of pharmacist intern and pharmacist extern if differentiation is not needed. (3-21-12)
05. Technician. Unless specifically differentiated, a term inclusive of pharmacy technician, certified pharmacy technician, and technician-in-training to indicate an individual authorized by registration with the Board to perform routine pharmacy support services under the supervision of a pharmacist. (3-21-12)
06. Telepharmacy. The use of telecommunications and information technologies in the practice of pharmacy to provide pharmaceutical care services to patients at a distance. (3-21-12)
07. Therapeutic Equivalent Drugs. Products assigned an “A” code by the FDA in the Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations (Orange Book). (3-21-12)
08. Unit Dose. Drugs packaged in individual, sealed doses with tamper-evident packaging (for example, single unit-of-use, blister packaging, unused injectable vials, and ampules). (3-21-12)
09. USP. United States Pharmacopeia. (3-21-12)
10. USP-NF. United State Pharmacopeia-National Formulary. (3-21-12)
11. VAWD — Verified Accredited Wholesale Distributor. An accreditation program for wholesale distributors offered through NABP. (3-21-12)
12. VDO — Veterinary Drug Outlet. A registered establishment that employs a qualified VDT to distribute prescription veterinary drugs pursuant to lawful orders of a veterinarian. (3-21-12)
13. VDT — Veterinary Drug Technician. A non-pharmacist qualified by registration with the Board to distribute prescription veterinary drugs in a VDO. (3-21-12)
14. Veterinary Drug Order. A lawful order by a veterinarian issued pursuant to the establishment of a veterinarian-patient-client relationship as recognized by the American Veterinary Medical Association. (3-21-12)
15. VIS. Vaccine Information Statement.
040.CERTIFIED PHARMACY TECHNICIAN REGISTRATION.
To be approved for registration as a certified pharmacy technician, a person must satisfy the following requirements: (3-21-12)
01. Age. Be at least eighteen (18) years of age unless a waiver is granted by the Board’s executive director; (3-21-12)
02. Education. Be a high school graduate or the recipient of a high school equivalency diploma unless a waiver is granted by the Board’s executive director; (3-21-12)
03. Personal Characteristics. Be of good moral character and temperate habits; and (3-21-12)
04. Certification. Have obtained and maintained certified pharmacy technician (CPhT) status through the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB), the Institute for Certification of Pharmacy Technicians (ICPT), or their successors unless qualified for a continuous employment exemption.
041.TECHNICIAN-IN-TRAINING REGISTRATION.
A person who has not obtained or maintained technician certification may apply for registration as a technician-in-training if the person satisfies all other requirements for registration as a technician. (3-21-12)
01. Duties. Upon registration, a technician-in-training may perform any of the duties allowed by statute or rule to be delegated to a registered technician under the supervision of a pharmacist. (3-21-12)
02. Renewal. The registration of a technician-in-training expires on June 30 and is renewable two times. (3-21-12)
03. Registration Expiration. Upon the final expiration of a technician-in-training registration, a person must satisfy the technician certification and registration requirements of these rules to be lawfully employed as, or otherwise perform the duties of, a technician.
410.VERIFICATION TECHNICIAN PROGRAM.
Only institutional pharmacies located within acute care hospitals may utilize a verification technician program. A verification technician program allows qualified technicians to verify the work of other technicians in the filling of floor and ward stock and unit dose distribution systems for patients whose orders have previously been reviewed and approved by a pharmacist. (3-21-12)
01. Written Program Filing. Prior to initiating a verification technician program, an institutional pharmacy must prepare a written program description that includes at least the following: (3-21-12)
a. The name of the pharmacist assigned as the coordinator of the verification technician program; (3-21-12)
b. A description of the duties of the coordinator sufficient to ensure and demonstrate compliance by the institutional pharmacy with these verification technician program rules; (3-21-12)
c. A description of the duties of technicians designated to perform the functions of verifying the work of other technicians; (3-21-12)
d. Identification of the types of drugs verification technicians are authorized to verify; (3-21-12)
e. A description of the specialized and advanced training that must be provided to each verification technician; and (3-21-12)
f. A description of the monitoring and evaluation processes used by the institutional pharmacy to ensure the ongoing competency of each verification technician. (3-21-12)
02. Program Requirements. Each institutional pharmacy utilizing a verification technician program must comply with the following requirements: (3-21-12)
a. A technician must neither be designated to perform, nor may the technician perform, verification functions without competently completing the required training. (3-21-12)
b. A verification technician may verify only manufacturer prepared or robotically prepared unit dose drugs identified in the written program description for floor or ward stock or unit dose distribution systems of pharmacist reviewed and approved drug orders for hospital patients. If either the alteration of a unit dose or the combination of unit doses is required, a pharmacist must verify the resulting unit dose alteration or combination of unit doses. (3-21-12)
c. The institutional pharmacy must conduct ongoing monitoring and evaluation of each verification technician to ensure the ongoing competency of the technician. (3-21-12)
d. For each verification technician, an institutional pharmacy utilizing a verification technician program must maintain records containing: (3-21-12)
i. The date the technician was designated; (3-21-12)
ii. The date the technician completed the required training; (3-21-12)
iii. The dates and results of each competency evaluation; and (3-21-12)
iv. The dates of, and reasons for, any suspension or revocation of the technician’s designation or other disciplinary action against the verification technician connected with the performance of the technician’s duties in the verification technician program. (3-21-12)
e. While on duty, each verification technician must wear identification that includes the title, “Verification Technician.” (3-21-12)
f. The duties of the verification technician program coordinator must include the supervision of verification technicians to ensure their duties are performed competently in a manner that protects patient safety. (3-21-12)
References
Idaho Administrative Code
http://adminrules.idaho.gov/rules/current/27/0101.pdf
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives