
Second Academic Year for Medication Safety Scholars Program
March 22, 2024
Really excited to share the news that we will be beginning the second academic year for the Emily Jerry Foundation‘s Medication Safety Scholars Program! This comprehensive distance education and virtual engagement program was developed and successfully implemented over the… Read More



North Carolina Scorecard
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
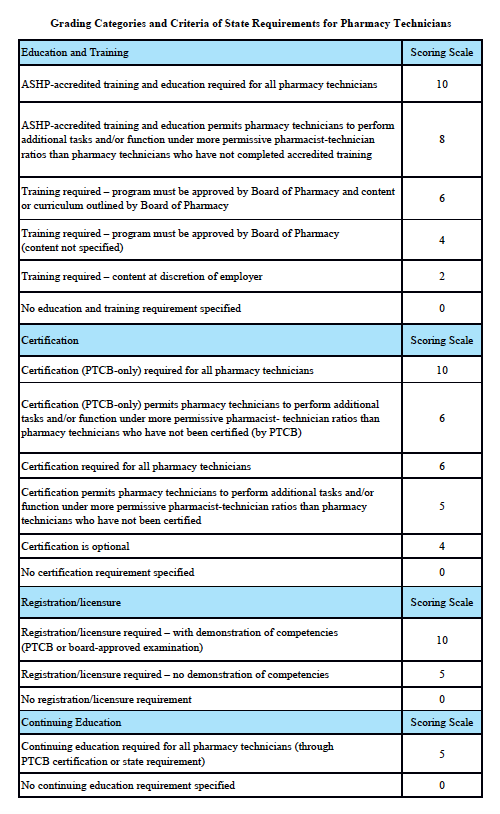
North Carolina Law
I. LAWS
http://www.ncbop.org/LawsRules/Statutes.pdf
§ 90-85.3. Definitions.
(q2) “Pharmacy technician” means a person who may, under the supervision of a pharmacist, perform technical functions to assist the pharmacist in preparing and dispensing prescription medications.
§ 90-85.15A. Pharmacy technicians.
(a) Registration. – A registration program for pharmacy technicians is established for the purposes of identifying those persons who are employed as pharmacy technicians. The Board must maintain a registry of pharmacy technicians that contains the name of each pharmacy technician, the name and location of the pharmacy in which the pharmacy technician works, the pharmacist-manager who employs the pharmacy technician, and the dates of that employment. The Board must register a pharmacy technician who pays the fee required under G.S. 90-85.24 and completes a required training program. A pharmacy technician must register with the Board within 30 days after the date the pharmacy technician completes a training program conducted by the pharmacy technician’s pharmacist-manager. The registration must be renewed annually by paying a registration fee.
(b) Responsibilities of Pharmacist-Manager. – A pharmacist-manager may hire a person who has a high school diploma or equivalent or is currently enrolled in a program that awards a high school diploma or equivalent to work as a pharmacy technician. Pursuant to G.S. 90-85.21, a pharmacist-manager must notify the Board within 30 days of the date the pharmacy technician began employment. The pharmacist-manager must provide a training program for a pharmacy technician that includes pharmacy terminology, pharmacy calculations, dispensing systems NCBOP—PHARMACY LAWS OF NORTH CAROLINA AS OF MARCH 2012 6 and labeling requirements, pharmacy laws and regulations, record keeping and documentation, and the proper handling and storage of medications. The requirements of a training program may differ depending upon the type of employment. The training program must be provided and completed within 180 days of the date the pharmacy technician began employment unless the pharmacy technician is registered with the Board. If the pharmacy technician is registered with the Board, then the completion of the training program is optional at the discretion of the pharmacist-manager.
(c) Supervision. – A pharmacist may not supervise more than two pharmacy technicians unless the pharmacist-manager receives written approval from the Board. The Board may not allow a pharmacist to supervise more than two pharmacy technicians unless the additional pharmacy technicians have passed a nationally recognized pharmacy technician certification board exam, or its equivalent, that has been approved by the Board. The Board must respond to a request from a pharmacist-manager to allow a pharmacist to supervise more than two pharmacy technicians within 60 days of the date it received the request. The Board must respond to the request in one of three ways:
(1) Approval of the request.
(2) Approval of the request as amended by the Board.
(3) Disapproval of the request. A disapproval of a request must include a reasonable explanation of why the request was not approved.
(d) Disciplinary Action. – The Board may, in accordance with Chapter 150B of the General Statutes and rules adopted by the Board, issue a letter of reprimand or suspend, restrict, revoke, or refuse to grant or renew the registration of a pharmacy technician if the pharmacy technician has done one or more of the following:
(1) Made false representations or withheld material information in connection with registering as a pharmacy technician.
(2) Been found guilty of or plead guilty or nolo contendere to a felony involving the use or distribution of drugs.
(3) Indulged in the use of drugs to an extent that it renders the pharmacy technician unfit to assist a pharmacist in preparing and dispensing prescription medications.
(4) Developed a physical or mental disability that renders the pharmacy technician unfit to assist a pharmacist in preparing and dispensing prescription medications.
(5) Willfully violated any provision of this Article or rules adopted by the Board governing pharmacy technicians.
(e) Exemption. – This section does not apply to pharmacy students who are enrolled in a school of pharmacy approved by the Board under G.S. 90-85.13.
(f) Rule-Making Authority. – The Board may adopt rules necessary to implement this section. (2001–375,
s. 2.)
§ 90-85.40. Violations.
(c) It shall be unlawful for any person not licensed as a pharmacist to compound or dispense any prescription drug, unless that person is a pharmacy technician or a pharmacy student who is enrolled in a school of pharmacy approved by the Board and is working under the supervision of a pharmacist.
NORTH CAROLINA ADMINISTRATIVE CODE
http://www.ncbop.org/LawsRules/Rules.pdf
21 NCAC 46 .1317 DEFINITIONS
(5) Certified technician. A technician who has passed a pharmacy technician certification board exam, or its equivalent, that has been approved by the Board according to the rules in this Chapter.
21 NCAC 46 .1418 SUPERVISION OF UNIT DOSE MEDICATION SYSTEMS
(a) The purpose of this Section is to set out requirements in the event that pharmacists elect to supervise designated pharmacy technicians’ validation of stocking and prepackaging functions in acute care hospital pharmacy practice settings as a means of facilitating pharmacists’ delivery of clinical services.
(b) A Hospital’s pharmacist-manager is responsible for the oversight of all validation of floor stock and unit dose distribution systems, and that responsibility may not be delegated pursuant to 21 NCAC 46 .1411. In the event that the Hospital’s pharmacist-manager elects to utilize Validating Technicians in the filling of floor stock and unit dose distribution systems, the pharmacist-manager shall develop written policies and procedures that:
(1) permit a Validating Technician to validate only the following functions of other registered pharmacy technicians in filling floor stock and unit dose distribution systems for inpatients in a Hospital:
(A) stocking of patient care unit medication inventories;
(B) stocking of ancillary drug cabinet inventories;
(C) stocking of automated dispensing or drug supply devices;
(D) stocking of emergency kits; and
(E) prepackaging of prescription drugs within the Hospital pharmacy;
(2) establish the parameters for pharmacist supervision of pharmacy technician validation functions;
(3) establish facility-specific training for pharmacy technician validation functions;
(4) establish an ongoing evaluation and assessment program to ensure that pharmacy technician validation functions are performed safely and accurately; and
(5) establish a recordkeeping system that shall permit the identification of the Validating Technician who performs activities authorized by this Rule. Readily retrievable records generated by this system shall be maintained for the period of time specified in 21 NCAC 46 .1414(j)(1) and (2).
(c) With respect to compounded or admixed prescription drugs (whether sterile or non-sterile), a Validating Technician may validate the filling of floor stock and unit dose distribution systems only after a pharmacist has verified that the compounded or admixed prescription drugs have been prepared correctly.
(d) This Rule does not authorize a pharmacy technician to perform any act requiring the exercise of professional judgment by a pharmacist.
(e) Validating Technician. For the purposes of this Rule, a Validating Technician shall be a pharmacy technician who:
(1) is registered with the Board and trained as specified in G.S. 90-85.15A;
(2) is a certified technician;
(3) holds either:
(A) an associate’s degree in pharmacy technology conferred by either an institution within the North
Carolina Community College System or System;
(B) an associate’s degree in pharmacy technology conferred by an institution accredited by one of the regional accrediting agencies recognized by the United States Department of Education; or
(C) an associate’s degree in pharmacy technology conferred by a program accredited by the American
Society of Health System Pharmacists; and
(4) assists pharmacists with the preparation, dispensing and distribution of prescription medications that will be administered by a licensed health care provider to an inpatient in a Hospital under this Rule.
(f) Hospital. For the purposes of this Rule, a Hospital is either:
(1) a hospital licensed by the North Carolina Medical Care Commission; or
(2) a psychiatric hospital operated by the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services.
(g) Pursuant to G.S. 90-85.15A(c), the Board approves a pharmacist’s supervision of more than two pharmacy technicians where the additional technicians are Validating Technicians. This Rule does not relieve the pharmacist-manager of the obligation to request and receive written Board approval for a pharmacist’s supervision of more than two pharmacy technicians where the additional technicians are certified pharmacy technicians but are not Validating Technicians.
(h) A pharmacy technician performing validation functions described in this Rule as part of a Board-approved
21 NCAC 46
.2510 pilot project at Broughton State Hospital or Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center may continue to perform
such functions for a period of three years from this Rule’s original effective date, after which time the pharmacy technician must meet all of the requirements specified in Paragraph (e) of this Rule to continue performing such functions.
History Note: Authority G.S. 90-85.6; 90-85.15A; 90-85.21; 90-85.26; 90-85.32; 90-85.33; 90-85.34;
Eff. June 18, 2011.
21 NCAC 46 .3301 REGISTRATION
(a) Following initial registration with the Board, registration of a pharmacy technician shall be renewed annually and shall expire on December 31. It shall be unlawful to work as a pharmacy technician more than 60 days after expiration of the registration without renewing the registration. A registration expired more than 60 days shall be reinstated pursuant to 21
NCAC 46 .1612.
(b) The current registration of a pharmacy technician shall be readily available for inspection by agents of the Board.
(c) The training program described in G.S. 90-85.15A(b) is not required for students enrolled in a community college pharmacy technician program.
(d) Volunteer pharmacy technicians providing services at a facility which has a pharmacy permit designated as a free clinic shall complete the training program described in G.S. 90-85.15A(b) but need not register with the Board.
(e) A pharmacist may not supervise more than two pharmacy technicians unless the additional pharmacy technicians have passed a national pharmacy technician certification examination administered by a provider whose examination assesses the ability of the technicians to function in accordance with G.S. 90-85.3(q2) and approved by the Board according to these standards.
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives