
Keynote at Mount Sinai Health System’s Medication Safety Together Summit
November 24, 2025
By ejfadmin
I was truly honored to represent the Emily Jerry Foundation last week at Mount Sinai Health System, where I had the privilege of delivering the keynote address to kick off their Medication Safety Together – An Interdisciplinary Summit… Read More



South Carolina Scorecard
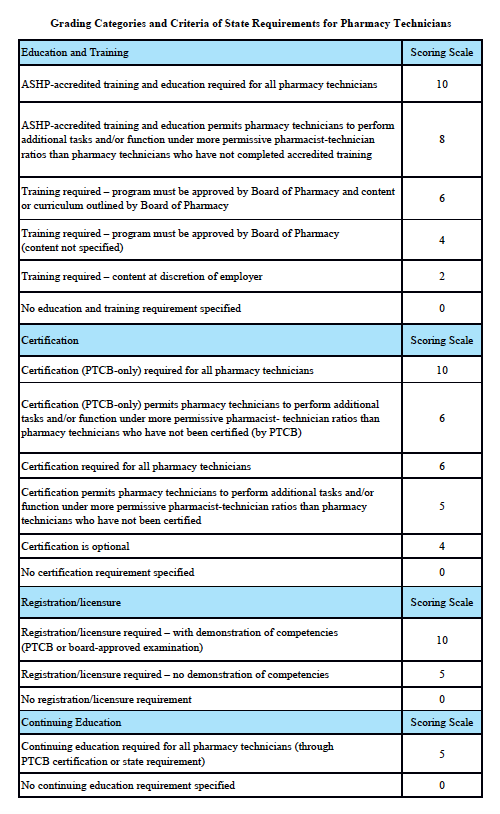
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
South Carolina Law
I. Laws
SOUTH CAROLINA CODE OF LAWS
http://www.scstatehouse.gov/code/t40c043.php
SECTION 40-43-30.Definitions.
(6) “”Certified pharmacy technician”” means an individual who is a registered pharmacy technician and who has completed the requirements provided for in Section 40-43-82(B).
(48) “”Pharmacy technician”” means an individual other than an intern or extern, who assists in preparing, compounding, and dispensing medicines under the personal supervision of a licensed pharmacist and who is required to register as a pharmacy technician.” “SECTION 40-43-60.Chief drug inspector; staff inspectors; duties; violation corrections or prosecution; duties of board; adulterated or misbranded drugs; destruction at owner’s expense; seal of drugs and devices under control of licensee when license suspended or revoked; complimentary drug samples; optometric supplies.
(D) The board shall:
(1) regulate the practice of pharmacy;
(2) regulate the sale and dispensing of drugs, poisons, and devices;
(3) regulate the supervision and training of pharmacy interns and technicians in pharmacies;” “SECTION 40-43-82.Pharmacy technicians; registration; approval of training programs; minimum requirements; pharmacists previously disciplined not eligible to be technicians; volunteers at free medical clinics.
(A)(1) The Board of Pharmacy shall register pharmacy technicians who are performing pharmacy functions under the supervision of a pharmacist.
(2) A registration is valid from July one through June thirtieth and is renewable on dates as prescribed by the department with the consent of the board. An application for renewal must be on a board approved form provided by the department and must be submitted and accompanied by an annual fee in an amount established in accordance with Section 40-1-50. A pharmacy technician who has failed to properly renew a registration before July first shall immediately cease practice and refrain from performing any duties as a pharmacy technician. Reinstatement of a registration must be granted upon the board receiving a renewal application and renewal and penalty fees.
(3) A pharmacy technician shall display his or her current registration in a conspicuous place in the primary pharmacy or drug outlet in which the technician is employed, so that the current registration is easily and readily observable by the public. A technician working in a pharmacy or drug outlet where the technician’s registration is not posted must have his or her wallet registration card with him or her.
(B)(1) An individual may be certified by the board as a pharmacy technician if the individual has:
(a) worked for fifteen hundred hours under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist as a registered pharmacy technician or has completed a Board of Pharmacy approved pharmacy technician course as provided for in subsection (D); however, beginning July 1, 2004, to be certified as a pharmacy technician an individual must have worked for one thousand hours under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist as a technician and must have completed a Board of Pharmacy approved technician course as provided for in subsection (D);
(b) a high school diploma or equivalent; and
(c) passed the National Pharmacy Technician Certification Board exam or a Board of Pharmacy approved exam and has maintained current certification; and
(d) fulfilled continuing education requirements as provided for in Section 40-43-130(G).
(2) The pharmacist-in-charge shall verify compliance with the requirements of item (a) of subsection (B)(1) and maintained a record of this requirement in a readily retrievable manner for inspection.
(C)(1) Notwithstanding any other provision of this chapter, a supervising pharmacist may authorize a certified pharmacy technician to perform any of the following actions including, but not limited to:
(a) receiving and initiating verbal telephone orders;
(b) conducting one-time prescription transfers;
(c) checking a technician’s refill of medications if the medication is to be administered by a licensed health care professional in an institutional setting; and
(d) checking a technician’s repackaging of medications from bulk to unit dose in an institutional setting.
(2) Nothing in this section prevents the Board of Pharmacy from establishing duties for a certified technician; provided, however, that a certified technician is prohibited from checking another technician’s fill, refill, or repackaging of medications for delivery to a patient in an outpatient setting.
(D) A formal academic pharmacy technician training program that leads to a certificate, diploma, or higher degree may be approved by the board if it includes at a minimum:
(1) introduction to pharmacy and health care systems;
(2) pharmacy law and ethics;
(3) pharmacy calculations;
(4) pharmacology;
(a) anatomy and physiology;
(b) therapeutic agents;
(c) prescription drugs;
(d) nonprescription drugs;
(5) pharmacy operations;
(a) drug distribution systems;
(b) records management and inventory control;
(c) ambulatory and institutional practice;
(6) compounding;
(a) aseptic technique;
(b) nonsterile compounding;
(7) general education;
(a) medical terminology;
(b) interpersonal relations;
(c) communications;
(d) computers/keyboarding;
(8) problem solving/critical thinking;
(9) experiential training (practical experience).
(E) A pharmacist whose license has been denied, revoked, suspended, or restricted for disciplinary purposes is not eligible to be registered as a pharmacy technician.
(F) Notwithstanding the requirements of this section or any other provision of law or regulation, an individual who works as an unpaid volunteer under the personal supervision of a licensed pharmacist or who handles legend drugs in a pharmacy department of a free medical clinic staffed by a licensed pharmacist may be registered as a pharmacy technician and may perform pharmacy functions as a pharmacy technician without payment of a registration fee or filing with the board; provided, that a register is maintained in the pharmacy department of the free medical clinic bearing the name of every such volunteer performing pharmacy functions as a pharmacy technician and documenting each volunteer’s period of service. This special registration is valid only in the free medical clinic. The register must be kept for a period of three years. For the purposes of this section, “”free medical clinic”” means a permitted facility that provides medical services, including the dispensing of legend drugs and other medications, free of any charge to members of the public.
(G) Pharmacy technicians are exempt from continuing education requirements for the first renewal period following initial registration.
HISTORY: 1998 Act No. 366, Section 1; 2000 Act No. 297, Section 1; 2002 Act No. 314, Section 4; 2017 Act No. 91 (H.3824), Sections 10.A, 10.B, eff May 19, 2017.
Effect of Amendment
2017 Act No. 91, Section 10.A, amended (C), prohibiting certain actions involving the filling, refilling, or repackaging of medications.
2017 Act No. 91, Section 10.B, added (G), providing that pharmacy technicians are exempt from continuing education requirements for a certain period.” “SECTION 40-43-130.Continuing education; topics; hours; carry over of hours; exemption period following examination; certificate of completion; authority to grant exemption for postgraduate degree work.
(G)(1) As a condition of registration renewal, a registered pharmacy technician shall complete ten hours of American Council on Pharmaceutical Education or CME I approved continuing education each year, beginning with the next renewal period after June 30, 2003.
(2) Topics and formats of study for continuing education must include subject matter designed to maintain the professional competence of pharmacy technicians registered with the board and to improve their professional skills in order to protect the public health and safety.
(3) Certification of completion of the required continuing education must be made on the annual registration renewal application, and no renewal may be issued without this certification. The board shall conduct an audit of continuing education credits of ten percent, randomly selected, of the total number of pharmacy technicians renewing.
(4) All hours completed in any registration year in excess of the requirements may be carried forward for credit in the next registration year but may not be carried forward for more than one registration year.
(H) Pharmacy technicians are exempt from continuing education requirements while enrolled in a pharmacy technician program, as well as during the first renewal period following successful completion of the program.
HISTORY: 1998 Act No. 366, Section 1; 2000 Act No. 340, Section 5; 2002 Act No. 314, Section 12; 2017 Act No. 91 (H.3824), Sections 9, 12, eff May 19, 2017; 2021 Act No. 48 (S.427), Sections 2, 3, eff May 17, 2021.
Effect of Amendment
2017 Act No. 91, Section 9, amended (B), adding requirements addressing certain controlled substances.
2017 Act No. 91, Section 12, added (H), relating to exemptions from continuing education requirements for pharmacy technicians.
2021 Act No. 48, Section 2, in (B), deleted the second sentence, which related to the minimum in-person continuing education requirements for pharmacists.
2021 Act No. 48, Section 3, in (G)(1), deleted the second sentence, which related to the minimum in-person continuing education requirements for pharmacy technicians.
South Carolina Board of Pharmacy Policy and Procedures
https://llr.sc.gov/bop/laws.aspx
State Certified Technician Education and Practical Experience Policy and Procedure #135
Per 40-43-82(B)(1)(a) a pharmacy technician applying to become a state certified technician must have worked for one thousand hours under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist as a technician and must have completed a Board-approved technician training course as provided for in 40-43-82(D). For purposes of this statute, a course that is either ASHP-accredited or PTCB-recognized is considered a Board approved course. All other courses must apply directly to the Board for evaluation. Pharmacy technicians submitting hours of practical experience for state certification must obtain those hours in a permitted facility under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist or in those sites that comply with the description listed in 40-43-85(G).
Approved Technician Duties Policy and Procedure #140
An employee of a pharmacy holding a pharmacy permit not registered with the SC Board of Pharmacy may perform many clerical functions associated with the practice of pharmacy. A non-registered employee is prohibited from performing the following functions:
• Entering data beyond demographic information (name, address, date of birth, gender, contact information, insurance, etc)
• Interpreting prescription drug orders
• Handling non-dispensed legend drugs or devices.
• Compounding of any over-the-counter or legend drug
A Registered or Certified Pharmacy Technician may perform many clerical functions associated with the practice of pharmacy at a facility holding a pharmacy permit. While fulfilling clerical functions, up to the point of dispensing requiring clinical interpretation and/or product selection, as defined in Section 40-43-30(15), registered or certified technicians would not be considered in the pharmacist to technician ratio as indicated by Sec. 40-43-86 (B)(4)(b).
A Registered Pharmacy Technician may perform many technical functions associated with the practice of pharmacy at a facility holding a pharmacy permit; however, even under the direct supervision of a pharmacist, the pharmacy technician is prohibited from performing the following functions:
• Performing any duty required by law or regulation to be performed by a state- certified technician, pharmacy intern or extern, or a pharmacist
• Administering immunizations
• Counseling a patient on a new or refill prescription
• Performing the final check on all aspects of the completed prescription
• Conducting or overriding a patient Drug Utilization Review and/or Drug Interaction Alerts
• Making clinical decisions based on medication reconciliation or history taking The following duties may be performed by a State Certified Registered Technician after the supervising pharmacist carefully considers the individual’s abilities and/or qualifications at a facility holding a pharmacy permit:
• Receiving and initiating verbal telephone orders for non-controlled prescriptions.
• Conducting a one-time transfer of a non-controlled prescription. This should in no way prohibit a future transfer of the same prescription.
• Checking a technician’s refill of medications if the medication is to be administered by a licensed healthcare professional in an institutional setting.
• Checking a technician’s repackaging of medications from bulk to unit dose in an institutional setting.
• Conducting monthly inspections of non-dispensing drug outlet permit sites, provided that inspection of the site does not require any clinical interpretation or review of patient charts or other patient-specific information, in which case the inspection must be completed by a pharmacist. A State Certified Registered Technician may not conduct inspections at any permitted site which engages in compounding. The consultant pharmacist of record shall conduct the inspection of the non-dispensing drug outlet permitted facility no less than every 6 months. If the inspection is conducted by a State Certified Registered Technician or another pharmacist, the consultant pharmacist must countersign the inspection form and send it to the non-dispensing permit site to retain for their records. The signed inspection form may be sent electronically. If a State Certified Registered Technician finds any deficiencies during the inspection, the person of contact at the permitted site must be contacted immediately and the consultant pharmacist must be notified within 24 hours.
As stated in Section 40-43-82(C), “…a certified technician is prohibited from checking another technician’s fill, refill, or repackaging of medications for delivery to a patient in an outpatient setting.”
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives