
EJF at Touro University’s College of Pharmacy in NYC for their Dean’s Hour Lecture
April 15, 2025
By ejfadmin
The week before last, I had the privilege of spending a few days in New York City to speak at a truly impactful Medication Safety Symposium hosted by Touro University’s College of Pharmacy. The following day, I was… Read More



Alaska Scorecard
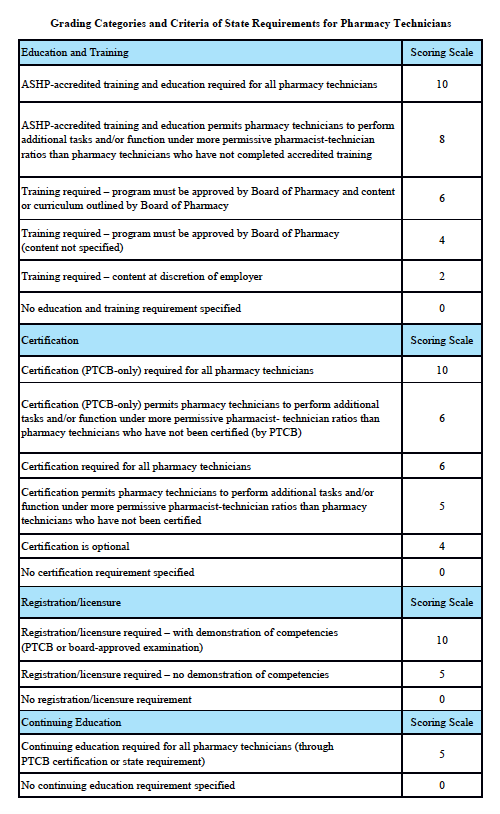
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
Alaska Law
I. Laws
30. Powers and duties of the board
160. Fees 480. Definitions
Sec. 08.80.030. POWERS AND DUTIES OF THE BOARD.
(a) The board is responsible for the control and regulation of the practice of pharmacy.
(b) In order to fulfill its responsibilities, the board has the powers necessary for implementation and enforcement of this chapter, including the power to
(1) elect a president and secretary from its membership and adopt rules for the conduct of its business;
(2) license by examination or by license transfer the applicants who are qualified to engage in the practice of pharmacy;
(3) assist the department in inspections and investigations for violations of this chapter, or of any other state or federal statute relating to the practice of pharmacy;
(4) adopt regulations to carry out the purposes of this chapter;
(5) establish and enforce compliance with professional standards and rules of conduct for pharmacists engaged in the practice of pharmacy;
(6) determine standards for recognition and approval of degree programs of schools and colleges of pharmacy whose graduates shall be eligible for licensure in this state, including the specification and enforcement of requirements for practical training, including internships;
(7) establish for pharmacists and pharmacies minimum specifications for the physical facilities, technical equipment, personnel, and procedures for the storage, compounding, and dispensing of drugs or related devices, and for the monitoring of drug therapy;
(8) enforce the provisions of this chapter relating to the conduct or competence of pharmacists practicing in the state, and the suspension, revocation, or restriction of licenses to engage in the practice of pharmacy;
(9) license and regulate the training, qualifications, and employment of pharmacy interns and pharmacy technicians;
(10) issue licenses to persons engaged in the manufacture and distribution of drugs and related devices;
(11) establish and maintain a controlled substance prescription database as provided in AS 17.30.200.
Sec. 08.80.160. FEES. The Department of Commerce, Community, and Economic Development shall set fees under AS 08.01.065 for the following:
(1) examination;
(2) reexamination;
(3) investigation for licensing by license transfer;
(4) pharmacist license;
(5) temporary license;
(6) pharmacy technician license;
(7) pharmacy intern license;
(8) emergency permit;
(9) license amendment or replacement;
(10) registration or licensure of a facility classified under AS 08.80.157(b).
Sec. 08.80.480. DEFINITIONS.
In this chapter, unless the context otherwise requires
(1) “administer” means the direct application of a drug to the body of a patient or research subject by injection, inhalation, ingestion, or other means;
(2) “board” means the Board of Pharmacy;
(3) “compounding” means the preparation, mixing, assembling, packaging, or labeling of a drug or device (A) as the result of a practitioner’s prescription drug order or initiative based on the relationship of the practitioner, patient, and pharmacist in the course of professional practice or (B) for the purpose of, or as an incident to, research, teaching, or chemical analysis and not for sale or dispensing; “compounding” also includes the preparation of drugs or devices in anticipation of prescription drug orders based on routine, regularly observed prescribing patterns;
(4) “controlled substance” has the meaning given in AS 11.71.900;
(5) “deliver” or “delivery” means the actual, constructive, or attempted transfer of a drug or device from one person to another, whether or not for consideration;
(6) “device” means an instrument, apparatus, implement, machine, contrivance, implant, or other similar or related article, including a component part or accessory, that is required under federal law to bear the label “Caution: Federal or state law requires dispensing by or on the order of a physician”;
(7) “dispense” or “dispensing” means the preparation and delivery of a drug or device to a patient or patient’s agent under a lawful order of a practitioner in a suitable container appropriately labeled for subsequent administration to, or use by, a patient;
(8) “distribute” means the delivery of a drug or device other than by administering or dispensing;
(9) “drug” means an article recognized as a drug in an official compendium, or supplement to an official compendium; an article intended for use in the diagnosis, cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease in man or animal; an article other than food, intended to affect the structure or function of the body of man or animal; and an article intended for use as a component of an article specified in this paragraph but does not include devices or their components, parts, or accessories;
(10) “drug regimen review” includes evaluation of the prescription drug order and patient record for
(A) known allergies;
(B) rational therapy-contraindications;
(C) reasonable dose and route of administration;
(D) reasonable directions for use;
(E) duplication of therapy;
(F) drug-drug, drug-food, and drug-disease interactions;
(G) adverse drug reactions; and
(H) proper utilization, including over- or under-utilization, and optimum therapeutic outcomes;
(11) “equivalent drug product” means a drug product that has the same established name, active ingredients, strength or concentration, dosage form, and route of administration and that is formulated to contain the same amount of active ingredients in the same dosage form and to meet the same compendia or other applicable standards for strength, quality, purity, and identity, but that may differ in characteristics such as shape, scoring configuration, packaging, excipients including colors, flavors, preservatives, and expiration time;
(12) “intern” means an individual who is
(A) currently licensed by this state to engage in the practice of pharmacy while under the personal supervision of a pharmacist and is satisfactorily progressing toward meeting the requirements for licensure as a pharmacist; or
(B) a graduate from a college of pharmacy who is currently licensed by the board for the purpose of obtaining practical experience as a requirement for licensure as a pharmacist; -8-
(13) “labeling” means the process of preparing and affixing a label to a drug container, exclusive, however, of the labeling by a manufacturer, packer, or distributor or a nonprescription drug or commercially packed legend drug or device;
(14) “legend drug” means a prescription drug;
(15) “manufacturing” means the production, preparation, propagation, conversion, or processing of a drug or device, either directly or indirectly, by extraction from a substance of natural origin or independently by means of chemical or biological synthesis, and includes packaging or repackaging of a substance or labeling or relabeling of its container, and the promotion and marketing of drugs or devices; “manufacturing” also includes the preparation and promotion of commercially available products from bulk compounds for resale by pharmacies, practitioners, or other persons;
(16) “nonprescription drug” means a nonnarcotic medicine or drug that may be sold without a prescription and that is prepackaged for use by the consumer and labeled in accordance with the requirements of the statutes and regulations of the state and the federal government;
(17) “outpatient dispensing” means dispensing drugs for administration outside of the hospital pharmacy’s control;
(18) “owner” means the owner of a place of business for wholesaling, retailing, compounding, or dispensing drugs, medicines, or poisons;
(19) “patient counseling” means the communication by the pharmacist of information, as defined in the regulations of the board, to the patient or care giver in order to improve therapy by ensuring proper use of drugs and devices;
(20) “person” has the meaning given in AS 01.10.060 and also includes a governmental agency;
(21) “pharmaceutical care” is the provision of drug therapy and other pharmaceutical patient care services intended to achieve outcomes related to the cure or prevention of a disease, elimination or reduction of a patient’s symptoms, or arresting or slowing of a disease process as defined in regulations of the board;
(22) “pharmacist” means an individual currently licensed by this state to engage in the practice of pharmacy;
(23) “pharmacist-in-charge” means a pharmacist who accepts responsibility for operation of a pharmacy in a manner that complies with laws and regulations applicable to the practice of pharmacy and the distribution of drugs and who is personally in charge of the pharmacy and the pharmacy’s personnel;
(24) “pharmacy” means a place in this state where drugs are dispensed and pharmaceutical care is provided and a place outside of this state that is subject to licensure or registration under AS 08.80.157(b);
(25) “pharmacy located outside of the state” means a pharmacy that prepares or mixes prescription drugs outside of the state, regardless of the location at which those drugs may be shipped, mailed, or delivered to the consumer;
(26) “pharmacy technician” means a supportive staff member who works under the immediate supervision of a pharmacist;
(27) “practice of pharmacy” means the interpretation, evaluation, and dispensing of prescription drug orders in the patient’s best interest; participation in drug and device selection, drug administration, drug regimen reviews, and drug or drug-related research; provision of patient counseling and the provision of those acts or services necessary to provide pharmaceutical care; and the responsibility for: compounding and labeling of drugs and devices except labeling by a manufacturer, repackager, or distributor of nonprescription drugs and commercially packaged legend drugs and devices; proper and safe storage of drugs and devices; and maintenance of proper records for them;
(28) “practitioner” means an individual currently licensed, registered, or otherwise authorized by the jurisdiction in which the individual practices to prescribe and administer drugs in the course of professional practice;
(29) “preceptor” means an individual who is currently licensed by the board, meets the qualifications as a preceptor under the regulations of the board, and participates in the instructional training of pharmacy interns;
(30) “prescription drug” means a drug that, under federal law, before being dispensed or delivered, is required to be labeled with either of the following statements:
(A) “Caution: Federal law prohibits dispensing without prescription”;
(B) “Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by, or on the order of, a licensed veterinarian”; or a drug that is required by an applicable federal or state law or regulation to be dispensed only under a prescription drug order or is restricted to use by practitioners only;
(31) “prescription drug order” means a lawful order of a practitioner for a drug or device for a specific patient;
(32) “prospective drug use review” means a review of the patient’s drug therapy and prescription drug order, as defined in the regulations of the board, before dispensing the drug as part of a drug regimen review;
(33) “significant adverse drug reaction” means a drug-related incident that may result in serious harm, injury, or death to the patient;
(34) “substitution” means to dispense without the prescriber’s expressed authorization, an equivalent drug product in place of the prescribed drug;
(35) “wholesale” means sale by a manufacturer, wholesale dealer, distributor, or jobber to a person who sells, or intends to sell, directly to the user:
(36) “wholesale drug distributor” means anyone engaged in wholesale distribution of drugs, including but not limited to manufacturers; repackagers; own-label distributors; private label distributors; jobbers; brokers; warehouses, including manufacturers’ and distributors’ warehouses; chain drug warehouses; wholesale drug warehouses; independent wholesale drug traders; and retail pharmacies that conduct wholesale distributions.
• Rules
10. Classifications of licensure
140. Pharmacy technician license
230. Pharmacy technicians
300. License renewal
310. Reinstatement of an expired pharmacist or pharmacy technician license
325. Continuing education requirements for pharmacy technicians
340. Approved programs
12 AAC 52.010. CLASSIFICATIONS OF LICENSURE.
(a) The board will issue the following categories of licenses or permits to a qualified individual:
(1) pharmacist license;
(2) temporary pharmacist license;
(3) emergency permit to practice pharmacy;
(4) pharmacist intern license;
(5) pharmacy technician license.
(b) The board will issue the following categories of licenses or registrations to a qualified facility:
(1) pharmacy license;
(2) repealed 2/26/2000;
(3) wholesale drug distributor license;
(4) drug room license;
(5) registration of a pharmacy located outside of the state;
(6) remote pharmacy license.
Authority: AS 08.80.005 AS 08.80.150 AS 08.80.158
-10-
AS 08.80.030 AS 08.80.155 AS 08.80.390
AS 08.80.116 AS 08.80.157
12 AAC 52.140. PHARMACY TECHNICIAN LICENSE.
(a) An applicant who meets the requirements on the checklist set out in (b) of this section has demonstrated the necessary qualifications for a pharmacy technician license. An applicant who does not meet the requirements on the checklist or whose responses on the form for application do not clearly show that the applicant is qualified to receive a pharmacy technician license will not be issued a license unless the board reviews the application and determines that the applicant meets the qualifications in this section for a pharmacy technician license.
(b) The following checklist is established by the board for review of an application for a pharmacy technician license; a pharmacy technician license will be issued to an applicant who
(1) submits a completed form for application, including
(A) the applicant’s name, mailing address, and telephone number; and
(B) the applicant’s date of birth that shows the applicant is at least 18 years old;
(2) certifies that the applicant has not been convicted of a felony or another crime that affects the applicant’s ability to perform the duties of a pharmacy technician safely and competently;
(3) certifies that the applicant has earned a high school diploma or its equivalent and provides the name of the issuing institution and the date the diploma or its equivalent was issued;
(4) certifies that the applicant is fluent in the reading, writing, and speaking of the English language; and
(5) pays the application fee and the pharmacy technician license fee established in 12 AAC 02.310.
(c) A pharmacy technician license expires on June 30 of even-numbered years and may be renewed.
12 AAC 52.230. PHARMACY TECHNICIANS.
(a) The following persons must be licensed as a pharmacy technician:
(1) any individual who assists in performing manipulative, nondiscretionary functions associated with the practice of pharmacy; and
(2) a supportive staff member assigned to work in the dispensing area of a pharmacy, including a cashier or a bookkeeper.
(b) A pharmacy technician shall work under the direct supervision of a person who is licensed as a pharmacist.
(c) A pharmacy technician may not perform any of the duties listed in 12 AAC 52.210.
(d) An individual working as a pharmacy technician shall wear an identification badge that shows the individual’s name and identifies the individual as a pharmacy technician.
(e) Before an individual may regularly perform the tasks of a pharmacy technician, the individual shall complete training required by the pharmacist-in-charge. Duties performed by the pharmacy technician must be consistent with the training the pharmacy technician has received.
(f) If a pharmacy technician will assist in the preparation of sterile pharmaceuticals, including parenteral medications, the pharmacy technician must have completed a minimum of 40 hours of on-the-job training in the preparation, sterilization, aseptic technique, and admixture of parenteral and other sterile pharmaceuticals before the pharmacy technician may regularly perform those tasks.
12 AAC 52.300. LICENSE RENEWAL.
(a) Pharmacy, wholesale drug distributor, and drug room licenses expire on June 30 of even-numbered years.
(b) An applicant for renewal of a pharmacy, wholesale drug distributor, or drug room license shall submit
(1) a completed renewal application;
(2) the license renewal fees required in 12 AAC 02.310; and
(3) a completed self-inspection of the premises questionnaire on a form provided by the department.
(c) An applicant for renewal of a pharmacist or pharmacy technician license shall submit on or before the license expiration date
(1) a completed renewal application;
(2) the license renewal fees required in 12 AAC 02.310;
(3) documentation that the applicant has met all continuing education requirements of 12 AAC 52.320 – 12 AAC 52.350; and
(4) if seeking renewal for a licensing period that begins on or after July 1, 2006, a completed jurisprudence questionnaire prepared by the board, covering the provisions of AS 08.80 and this chapter.
Authority: AS 08.01.100 AS 08.80.030 AS 08.80.157
AS 08.80.005 AS 08.80.147 AS 08.80.165
12 AAC 52.310. REINSTATEMENT OF AN EXPIRED PHARMACIST OR PHARMACY TECHNICIAN LICENSE.
(a) If a pharmacist’s or pharmacy technician’s license has expired for any reason, that pharmacist or pharmacy technician may not practice pharmacy until the license is reinstated by the board.
(b) The board will reinstate a pharmacist or pharmacy technician license that has been expired less than two years if the applicant submits
(1) a completed renewal application;
(2) any applicable license renewal fees required in 12 AAC 02.310;
(3) documentation that the applicant has met all continuing education requirements of 12 AAC 52.320 – 12 AAC 52.350; and
(4) for a licensing period that begins on or after July 1, 2006, a completed jurisprudence questionnaire prepared by the board, covering the provisions of AS 08.80 and this chapter.
(c) The board will reinstate a pharmacist license that has been expired at least two years but not more than five years if the applicant
(1) submits a completed application for reinstatement on a form provided by the department;
(2) pays any applicable license renewal fees required in 12 AAC 02.310 for the entire period the license has been expired;
(3) repealed 5/5/00;
(4) submits evidence of completion of all continuing education requirements in 12 AAC 52.320 – 12 AAC 52.350 that would have been required to maintain a current license for the entire period the license has been expired;
(5) qualifies by
(A) retaking and passing the examinations required in 12 AAC 52.090(a); or -19-
(B) providing verification that the applicant has continually practiced pharmacy in another state under a license issued by the authority of that state for the period that the license has been expired, and by meeting the requirements of 12 AAC 52.090(a)(2); for purposes of AS 08.80.147 and this subparagraph, an applicant has continually practiced pharmacy if the pharmacist has actively practiced pharmacy in the other state for at least six months during each year that the license in this state was lapsed; and
(6) submits a verification issued directly to the board by each licensing jurisdiction where the applicant holds, or has ever held, a license as a pharmacist during the time period in which the applicant’s license was lapsed in this state that the applicant’s license in the other jurisdiction were not suspended, revoked, or otherwise restricted except for failure to apply for renewal or failure to obtain the required continuing education requirements; or a copy of the applicant’s Official Application for Transfer of Pharmaceutics Licensure, sent directly to the department from the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy not later than 90 days of the date of issue.
(d) The board will reinstate a pharmacist license that has been expired for five years or more if the applicant
(1) submits a completed application for reinstatement on a form provided by the department;
(2) pays any applicable license renewal fees required in 12 AAC 02.310 for the entire period the license has been expired;
(3) repealed 5/5/00; and
(4) qualifies by
(A) retaking and passing the examinations required in 12 AAC 52.090(a);
(B) providing verification that the applicant has continually practiced pharmacy in another state under alicense issued by the authority of that state for the period that the license has been expired, and by meeting the requirements of 12 AAC 52.090(a) (2); for purposes of AS 08.80.147 and this subparagraph, an applicant has continually practiced pharmacy if the pharmacist has actively practiced pharmacy in the other state for at least six months during each year that the license in this state was expired; or
(C) submitting verification from each licensing jurisdiction where the applicant holds, or has ever held, a license as a pharmacist during the time period in which the applicant’s license was lapsed in this state that the applicant’s license in the other jurisdiction were not suspended, revoked, or otherwise restricted except for failure to apply for renewal or failure to obtain the required continuing education requirements; or a copy of the applicant’s Official Application for Transfer of Pharmaceutics Licensure, sent directly to the department from the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy not later than 90 days of the date of issue.
(e) A pharmacy technician license that has been expired for two years or more will not be reinstated.
Authority: AS 08.01.100 AS 08.80.030 AS 08.80.165 AS 08.80.005 AS 08.80.147
12 AAC 52.325. CONTINUING EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS FOR PHARMACY TECHNICIANS.
(a) Except as provided in (c) of this section, an applicant for renewal of a pharmacy technician license shall certify that, during the concluding licensing period, the applicant
(1) completed 10 contact hours of continuing education accepted by the board under 12 AAC 52.340; or
(2) obtained initial certification as a pharmacy technician by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).
(b) This section does not prevent the board from imposing additional continuing education requirements under its disciplinary powers.
(c) Instead of complying with the continuing education requirements in (a) of this section, an applicant for renewal of a pharmacy technician license for the first time may
(1) verify in an affidavit, on an application for renewal, that the applicant has read the state statutes and regulations compiled by the board; and
(2) submit an affidavit, signed by the pharmacist-in-charge, verifying the applicant’s pharmacy technician training in accordance with 12 AAC 52.230.
(d) An applicant for reinstatement of a pharmacy technician license that has expired shall certify that the applicant completed the continuing education requirements in (a) of this section before applying for reinstatement.
-20-
Authority: AS 08.01.100 AS 08.80.030 AS 08.80.165
AS 08.80.005
Editor’s note: Information regarding certification with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board described in 12 AAC 52.325 may be obtained from the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board, 1100 15th Street, NW, Suite 703, Washington, DC 20005-1707, phone: (202) 429-4120 or at PTCB’s website at www.ptcb.org. The Alaska Pharmacists Association, 203 West 15th Avenue, #100, Anchorage, AK 99501, phone: (907) 563-8880, email: akphrmcy@alaska.net also provides certification information.
12 AAC 52.340 APPROVED PROGRAMS.
(a) The following programs will be accepted by the board as continuing education for pharmacists and pharmacy technicians under 12 AAC 52.320 and 12 AAC 52.325:
(1) any program presented by a provider accredited by the ACPE;
(2) cardiopulmonary resuscitation(CPR) courses presented by the American Red Cross or the American Heart Association that lead to CPR certification; the board will accept no more than one contact hour of continuing education credit in a 24 month period for completion of a CPR course.
(b) The following programs will be accepted by the board as continuing education under 12 AAC 52.325, when the subject contributes directly to the professional competency of a pharmacy technician and is directly related to pharmacy principles and practice:
(1) any program presented or approved by the Alaska Pharmacists Association;
(2) any program presented or approved by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) or the National Pharmacy Technician Association (NPTA).
(c) An individual who presents an approved continuing education program may receive credit for the time spent during the actual presentation of the program. An individual may not receive credit for the same presentation more than once during a licensing period.
Authority: AS 08.80.005 AS 08.80.147 AS 08.80.165
AS 08.80.030
References
Statutes and Regulations December 2011
http://www.dced.state.ak.us/occ/pub/PharmacyStatutes.pdf
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives