
Happy Heavenly 22nd Birthday Emily + Upcoming Pacific Coast Patient Safety Conference
February 24, 2026
By ejfadmin
Tomorrow, I’m really looking forward to heading to Monterey, California to speak on behalf of the Emily Jerry Foundation at the Pacific Coast Patient Safety Conference, hosted by the California Society of Health – System Pharmacists. But today… Read More



California Scorecard
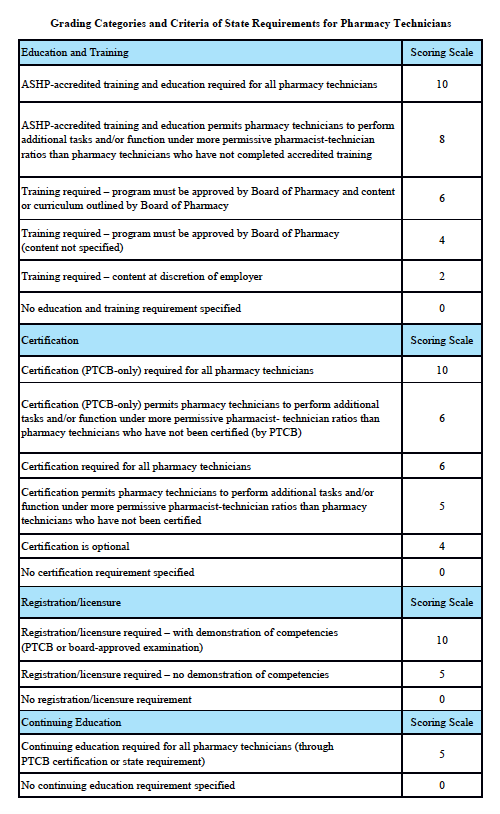
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
California Law
I. Statutes (Laws)
Section 4038
Section 4115
Section 4202
https://www.pharmacy.ca.gov/laws_regs/pharmacy_lawbook.shtml
4115. Pharmacy Technician: Activities Permitted; Required Supervision; Activities Limited to Pharmacist; Registration; Requirements for Registration; Ratio
(a) A pharmacy technician may perform packaging, manipulative, repetitive, or other nondiscretionary tasks, only while assisting, and while under the direct supervision and control of a pharmacist. The pharmacist shall be responsible for the duties performed under their supervision by a technician.
(b)(1) In addition to the tasks specified in subdivision (a) a pharmacy technician may, under the direct supervision and control of a pharmacist, prepare and administer influenza and COVID-19 vaccines via injection or intranasally, prepare and administer epinephrine, perform specimen collection for tests that are classified as waived under CLIA, receive prescription transfers, and accept clarification on prescriptions under the following conditions:
(A) The pharmacy has scheduled another pharmacy technician to assist the pharmacist by performing the tasks provided in subdivision (a).
(B) The pharmacy technician is certified pursuant to paragraph (4) of subdivision (a) of Section 4202 and maintains that certification.
(C) The pharmacy technician has successfully completed at least six hours of practical training approved by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education and includes hands-on injection technique, the recognition and treatment of emergency reactions to vaccines, and an assessment of the pharmacy technician’s
injection technique.
(D) The pharmacy technician is certified in basic life support.
(2) “CLIA” means the federal Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (42 U.S.C. Sec. 263a; Public Law 100-578).
(c) This section does not authorize the performance of any tasks specified in subdivisions (a) and (b) by a pharmacy technician without a pharmacist on duty.
(d) This section does not authorize a pharmacy technician to perform any act requiring the exercise of professional judgment by a pharmacist.
(e) The board shall adopt regulations to specify tasks pursuant to subdivision (a) that a pharmacy technician may perform under the supervision of a pharmacist. Any pharmacy that employs a pharmacy technician shall do so in conformity with the regulations adopted by the board.
(f) No person shall act as a pharmacy technician without first being licensed by the board as a pharmacy technician.
(g) (1) A pharmacy with only one pharmacist shall have no more than one pharmacy technician performing the tasks specified in subdivision (a). A pharmacy with only one pharmacist shall have no more than one pharmacy technician performing the tasks specified in subdivision (b). If a pharmacy technician is performing the tasks specified in subdivision (b), a second pharmacy technician shall be assisting a pharmacist with performing tasks specified in subdivision (a). The ratio of pharmacy technicians performing the tasks specified in subdivision (a) to any additional pharmacist shall not exceed 2:1, except that this ratio shall not apply to personnel performing clerical functions pursuant to Section 4116 or 4117. This ratio is applicable to all practice settings, except for an inpatient of a licensed health facility, a patient of a licensed home health agency, as specified in paragraph (2), an inmate of a correctional facility of the Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation, and for a person receiving treatment in a facility operated by the State Department of State Hospitals, the State Department of Developmental Services, or the Department of Veterans Affairs.
(2) The board may adopt regulations establishing the ratio of pharmacy technicians performing the tasks specified in subdivision (a) to pharmacists applicable to the filling of prescriptions of an inpatient of a licensed health facility and for a patient of a licensed home health agency. Any ratio established by the board pursuant to this subdivision shall allow, at a minimum, at least one pharmacy technician for a single pharmacist in a pharmacy and two pharmacy technicians for each additional pharmacist, except that this ratio shall not apply to personnel performing clerical functions pursuant to Section 4116 or 4117.
(3) A pharmacist scheduled to supervise a second pharmacy technician may refuse to supervise a second pharmacy technician if the pharmacist determines, in the exercise of their professional judgment, that permitting the second pharmacy technician to be on duty would interfere with the effective performance of the pharmacist’s responsibilities under this chapter. A pharmacist assigned to supervise a second pharmacy technician shall notify
the pharmacist-in-charge in writing of their determination,
specifying the circumstances of concern with respect to the
pharmacy or the pharmacy technician that have led to the
determination, within a reasonable period, but not to exceed 24
hours, after the posting of the relevant schedule. No entity
employing a pharmacist may discharge, discipline, or otherwise
discriminate against any pharmacist in the terms and conditions
of employment for exercising or attempting to exercise in good
faith the right established pursuant to this paragraph.
(h) Notwithstanding subdivisions (a) to (c), inclusive, the board
shall by regulation establish conditions to permit the temporary
absence of a pharmacist for breaks and lunch periods pursuant to
Section 512 of the Labor Code and the orders of the Industrial
Welfare Commission without closing the pharmacy. During these
temporary absences, a pharmacy technician may, at the discretion of the pharmacist, remain in the pharmacy but may
only perform nondiscretionary tasks. The pharmacist shall be
responsible for a pharmacy technician and shall review any task
performed by a pharmacy technician during the pharmacist’s
temporary absence. Nothing in this subdivision shall be
construed to authorize a pharmacist to supervise pharmacy
technicians in greater ratios than those described in subdivision
(g).
(i) The pharmacist on duty shall be directly responsible for the
conduct of a pharmacy technician supervised by that pharmacist.
(j) In a health care facility licensed under subdivision (a) of
Section 1250 of the Health and Safety Code, a pharmacy
technician’s duties may include any of the following:
(1) Packaging emergency supplies for use in the health care
facility and the hospital’s emergency medical system or as
authorized under Section 4119.
(2) Sealing emergency containers for use in the health care
facility.
(3) Performing monthly checks of the drug supplies stored
throughout the health care facility. Irregularities shall be
reported within 24 hours to the pharmacist-in-charge and the
director or chief executive officer of the health care facility in
accordance with the health care facility’s policies and
procedures.
4202. Pharmacy Technician: License Requirements for Education, Experience; Board Regulations; Criminal Background Check; Discipline
(a) The board may issue a pharmacy technician license to an
individual if the applicant is a high school graduate or possesses a
general educational development certificate equivalent, and
meets any one of the following requirements:
(1) Has obtained an associate’s degree in pharmacy technology.
(2) Has completed a course of training specified by the board.
(3) Has graduated from a school of pharmacy recognized by the
board.
(4) Is certified by a pharmacy technician certifying organization
offering a pharmacy technician certification program accredited
by the National Commission for Certifying Agencies that is
approved by the board.
(b) The board shall adopt regulations pursuant to this section for
the licensure of pharmacy technicians and for the specification of
training courses as set out in paragraph (2) of subdivision (a).
Proof of the qualifications of any applicant for licensure as a
pharmacy technician shall be made to the satisfaction of the
board and shall be substantiated by any evidence required by the
board.
(c) The board shall conduct a criminal background check of the
applicant to determine if an applicant has committed acts that
would constitute grounds for denial of licensure, pursuant to this
chapter or Chapter 2 (commencing with Section 480) of Division
1.5.
(d) The board shall not renew a pharmacy technician license
unless the applicant submits proof satisfactory to the board that
the applicant has successfully completed at least one hour of
participation in a cultural competency course, as defined in
Section 4231, during the two years preceding the application for
renewal.
(e) The board may suspend or revoke a license issued pursuant
to this section on any ground specified in Section 4301.
(f) Once an individual is licensed as a pharmacist, the pharmacy
technician registration is no longer valid and the pharmacy
technician license shall be returned to the board within 15 days.
(g) This section shall become operative on January 1, 2024.
Article 4 Continuing Education
1732.8. Renewal Requirements for Pharmacy Technicians.
(a) As a condition of license renewal, a pharmacy technician
licensee shall submit proof satisfactory to the Board that the
applicant has completed at least one (1) hour of continuing
education (CE) in a cultural competency course covering the
specified content areas, from an accreditation agency approved
by the Board pursuant to section 1732.05, during the two years
preceding the application for renewal, as required by section
4202 of the Business and Professions Code. All pharmacy
technicians shall retain their certificate of completion for four (4)
years from the date of completion of the cultural competency course to demonstrate compliance with the provisions of this
section.
(b) If an applicant for renewal of a pharmacy technician license
submits the renewal application and payment of the renewal fee
but does not submit proof satisfactory to the Board that the
licensee has completed the cultural competency course as
required, the Board shall not renew the license and shall issue
the applicant an inactive pharmacy technician license.
(c) If, as part of an investigation or audit conducted by the Board,
a pharmacy technician fails to provide documentation
substantiating the completion of CE as required in subsection (a),
the Board shall cancel the active pharmacy technician license and
issue an inactive pharmacy technician license in its place. A
licensee with an inactive pharmacy technician license issued
pursuant to this section may obtain an active pharmacy
technician license by submitting renewal fees due and submitting
proof satisfactory to the Board that the pharmacy technician has
completed the required CE.
NOTE: Authority cited: Sections 462 and 4005, Business and
Professions Code. Reference: Sections 462 and 4202, Business
and Professions Code.
Regulations
Change California Code of Regulations Title 16, Division 17 link to:
https://govt.westlaw.com/calregs/Browse/Home/California/CaliforniaCodeofRegulations?guid=IC5E42C404C8111EC89E5000D3A7C4BC3&originationContext=documenttoc&transitionType=Default&contextData=(sc.Default)”
1793.5. Pharmacy Technician Application.
The “Pharmacy Technician Application (Form 17A-5 (Rev. 12/2021)), incorporated by reference herein, required by this section is available from the Board of Pharmacy upon request.” “1793.5. Pharmacy Technician Application.
The “Pharmacy Technician Application (Form 17A-5(Rev. 01/11)), incorporated by reference herein, required by this section is available from the Board of Pharmacy upon request.
(a) Each application for a pharmacy technician license shall include:
(1) Information sufficient to identify the applicant.
(2) A description of the applicant’s qualifications, and supporting documentation for those qualifications.
(3) A criminal background check that will require submission of fingerprints in a manner specified by the board and the fee authorized in Penal Code section 11105(e).
(4) A sealed, original Self-Query from the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) dated no earlier than 60 days of the date an application is submitted to the board.
(b) The applicant shall sign the application under penalty of perjury and shall submit it to the Board of Pharmacy.
(c) The board shall notify the applicant within 30 days if an application is deficient; and what is needed to correct the deficiency. Once the application is complete, and upon completion of any investigation conducted pursuant to section 4207 of the Business and Professions Code, the board will notify the applicant within 60 days of a license decision.
(d) Before expiration of a pharmacy technician license, a pharmacy technician must renew that license by payment of the fee specified in subdivision (r) of section 4400 of the Business and Professions Code.” “1793.6. Training Courses Specified by the Board.
A course of training that meets the requirements of Business and Professions Code section 4202 (a)(2) is:
(a) Any pharmacy technician training program accredited by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists,
(b) Any pharmacy technician training program provided by a branch of the federal armed services for which the applicant possesses a certificate of completion, or
(c)(1) Any other course that provides a training period of at least 240 hours of instruction covering at least the following:
(A) Knowledge and understanding of different pharmacy practice settings.
(B) Knowledge and understanding of the duties and responsibilities of a pharmacy technician in relationship to other pharmacy personnel and knowledge of standards and ethics, laws and regulations governing the practice of pharmacy.
(C) Knowledge and ability to identify and employ pharmaceutical and medical terms, abbreviations and symbols commonly used in prescribing, dispensing and record keeping of medications.
(D) Knowledge of and the ability to carry out calculations required for common dosage determination, employing both the metric and apothecary systems.
(E) Knowledge and understanding of the identification of drugs, drug dosages, routes of administration, dosage forms and storage requirements.
(F) Knowledge of and ability to perform the manipulative and record-keeping functions involved in and related to dispensing prescriptions.
(G) Knowledge of and ability to perform procedures and techniques relating to manufacturing, packaging, and labeling of drug products.
(2) In addition to the content of coursework specified in subdivision (c)(1), the course of training must also satisfy all of the following:
(A) Prior to enrollment in any classes or admission into the course of training, an administrator or instructor shall inform applicants of the criminal background check required for a pharmacy technician license per Business and Professions Code section 4202(c). An administrator or instructor shall counsel applicants about the negative impact to securing licensure if the criminal background check reveals that the applicant has committed acts that would constitute grounds for denial of licensure.
(B) Prior to enrollment in any classes or admission into the course of training, an administrator or instructor shall inform applicants that the course of training includes practical training at a pharmacy which may require the applicant to undergo drug screening for illicit drug use. The administrator or instructor shall counsel applicants about the negative impact of a positive drug screen, including eligibility to continue the course of training and eligibility for licensure.
(C) Require students to be at least 18 years of age prior to enrolling in any course work involving practical training, such as an externship or any other training equivalent to pharmacy technician trainee placement as defined by Business and Professions Code section 4038, 4115, 4115, and 4115.5.
(D) Require a final examination that demonstrates students’ understanding and ability to perform or apply each subject area identified in subdivision (1) above.
Authority cited: Sections 4005, and 4202, Business and Professions Code. Reference: Sections 4005, 4007, 4038, 4115 and 4202, Business and Professions Code.” “Add:
1793.65. Pharmacy Technician Certification Programs Approved by the Board.
(a) Pursuant to Business and Professions Code section 4202(a)(4), the Board approves the pharmacy technician certification program offered by:
(1) The Pharmacy Technician Certification Board, and
(2) The National Healthcareer Association.
(b) Approval of these programs is valid through June 30, 2026.
Authority cited: Sections 4005 and 4202, Business and Professions Code. Reference: Sections 4038 and 4202, Business and Professions Code.
III. References
California 2012 LAWBOOK FOR PHARMACY
http://www.pharmacy.ca.gov/laws_regs/lawbook.pdf
California Code of Regulations Title 16, Division 17
http://weblinks.westlaw.com/toc/default.aspx?Abbr=ca%2Dadc&Action=ExpandTree&AP=I2F03BEC0D48F11DEBC02831C6D6C108E&ItemKey=I2F03BEC0D48F11DEBC02831C6D6C108E&RP=%2Ftoc%2Fdefault%2Ewl&Service=TOC&RS=WEBL12.04&VR=2.0&SPa=CCR-1000&pbc=DA010192&fragment#I2F03BEC0D48F11DEBC02831C6D6C108E
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives