
Second Academic Year for Medication Safety Scholars Program
March 22, 2024
Really excited to share the news that we will be beginning the second academic year for the Emily Jerry Foundation‘s Medication Safety Scholars Program! This comprehensive distance education and virtual engagement program was developed and successfully implemented over the… Read More



Montana Scorecard
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
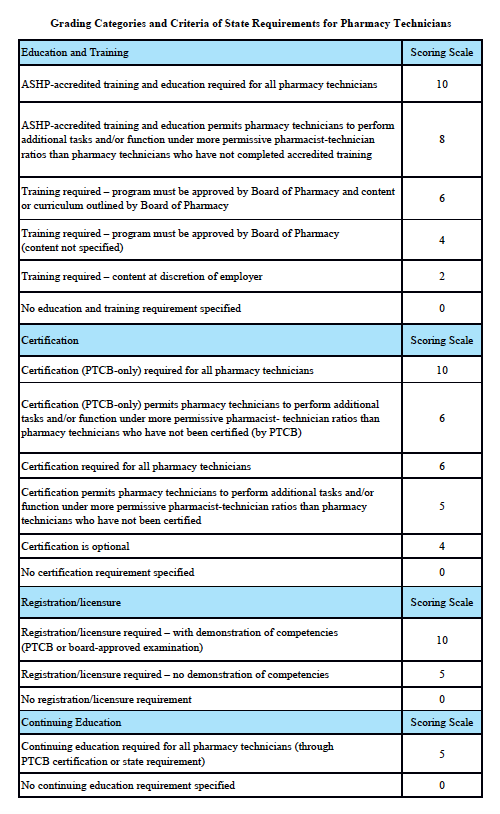
Montana Law
I. Laws
Montana Code Annotated (MCA) (Statutes/Laws)
Title 37 Professions and Occupations
Chapter 7 Pharmacy http://data.opi.mt.gov/bills/mca_toc/37_7.htm
Part 3. Licensing
37-7-301. Unlawful practice. Except as provided in 37-7-307 through 37-7-309, it is unlawful for a person to:
(1) engage in the practice of pharmacy unless licensed by the board; or
(2) assist in the practice of pharmacy unless registered by the board as a pharmacy technician.
Montana Rules
DEPARTMENT OF LABOR AND INDUSTRY
CHAPTER 174
BOARD OF PHARMACY
Rule: 24.174.7 – Pharmacy Technicians http://bsd.dli.mt.gov/license/bsd_boards/pha_board/pdf/pha_rules.pdf
24.174.701 REGISTRATION REQUIREMENTS
(1) In order to be registered as a pharmacy technician in this state, the applicant shall:
(a) submit application on a form prescribed by the board;
(b) pay application fees as prescribed by the board; and
(c) submit a copy of proof of certification by PTCB or other board approved certifying entity.
(2) In order to be registered as a technician-in-training in this state, the applicant shall:
(a) apply to the board for a permit on an application supplied by the board;
(b) pay the fee required;
(c) provide the name and address of the pharmacy in which the technician-in-training is employed. A change in place of employment will require submission of updated information within ten working days of the change.
(3) The permit to practice as a technician-in-training shall be valid for a period of not longer than 18 months. A technician-in-training applicant who has not passed the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB), ExCPT, or other board-approved certifying exam within the 18 months due to extenuating circumstances may file a written request to the board for an extension of his or her technician-in-training license. The board will then determine when the license will expire. A technician-in-training whose license has expired but who did not pass the requisite exam may not apply for a technician-in-training license a second time.
(4) Working as a technician-in-training with an expired license is cause for disciplinary action against the licensee.
History: 37-7-201, MCA, IMP, 37-7-201, MCA; NEW, 2002 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; AMD, 2010 MAR p. 74, Eff. 1/15/10.
24.174.702 QUALIFICATIONS OF PHARMACY TECHNICIAN
(1) A person who acts as a pharmacy technician under the provisions of a utilization plan must be:
(a) at least 18 years old;
(b) a high school graduate or have attained an equivalent degree;
(c) of good moral character; and
(d) certified by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) or other board approved certifying entity.
(2) No pharmacist whose license has been denied, revoked, suspended, or restricted for disciplinary purposes shall be eligible to be registered as a pharmacy technician.
History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-7-201, 37-7-301, 37-7-307, MCA; NEW, 1992 MAR p. 1608, Eff. 7/31/92; AMD, 2001 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; TRANS, from Commerce, 2002 MAR p. 904.
24.174.703 USE OF PHARMACY TECHNICIAN
(1) A pharmacy technician may not perform tasks which require the exercise of the pharmacist’s independent professional judgment, including but not limited to, patient counseling, drug product selection, drug interaction review or drug regimen review.
(2) When a pharmacist is not in the prescription department, there shall be no dispensing of new prescriptions that the pharmacist has checked and that are waiting to be picked up, nor shall counseling be provided by the pharmacy technician.
(3) No medication may be released to a patient without review by a registered pharmacist for the accuracy and appropriateness of the prescription drug order.
(4) All technicians and auxiliary staff shall be made visually identifiable by name and job title utilizing letters of 16 point or larger on a name badge.
(5) All pharmacy technician licenses and technician-in-training permits must be conspicuously displayed at all times in the place of business.
History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-7-101, 37-7-201, 37-7-301, 37-7-307, MCA; NEW, 1992 MAR p. 1608, Eff. 7/31/92; AMD, 2000 MAR p. 2005, Eff. 7/28/00; AMD, 2002 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; TRANS, from Commerce, 2002 MAR p. 904; AMD, 2010 MAR p. 74, Eff. 1/15/10.
24.174.704 PHARMACY TECHNICIAN TRAINING
(1) A supervising pharmacist shall:
(a) provide initial training to a pharmacy technician that relates to the tasks the technician may perform pursuant to the supervising pharmacist’s utilization plan; and
(b) prepare and maintain a written record of initial and inservice training for on-site inspection by the board. The record shall contain the following information:
(i) name and signature of the person receiving the training;
(ii) dates of the training;
(iii) general description of the topics covered; and
(iv) name and signature of the person supervising the training.
(2) An initial training program must include on-the-job practical training and didactic education that is commensurate with the tasks and functions a pharmacy technician may perform. A supervising pharmacist must obtain the board’s approval of an initial training program prior to undertaking the training of a pharmacy technician pursuant to the program.
(3) Verification of completion of training, by test or otherwise, shall be recorded by the supervising pharmacist, and shall be available for inspection with the training record.
History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-7-201, 37-7-307, MCA; NEW, 1992 MAR p. 1608, Eff. 7/31/92; AMD, 2002 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; TRANS, from Commerce, 2002 MAR p. 904.
24.174.705 TASKS AND FUNCTIONS OF PHARMACY TECHNICIAN
(1) Only a registered pharmacy technician may perform the following tasks or functions under the provisions of an approved utilization plan:
(a) remove a stock bottle from the shelf and count or pour the contents into a suitable container. The stock bottle must be quarantined together with the prescription until the supervising pharmacist performs a final check or bar coding or other available technology verifies the bottle contents;
(b) type a prescription label and affix it and auxiliary labels to a prescription bottle, with final review by the registered pharmacist;
(c) enter prescription information into an automated system under the supervision of a pharmacist who must be able to check all entries;
(d) maintain prescription records, including prescription numbers, refill data and other information on the patient profile system;
(e) prepackage unit dose drugs for internal distribution. These prepackage unit dose drugs must be quarantined together with bulk containers until the supervising pharmacist performs a final check and maintains appropriate records.
(f) answer the telephone, properly identify themselves as a technician, accept verbal orders for refill prescriptions from medical practitioners or their designated agents and issue refill requests to the prescriber;
(g) a pharmacy technician may act as agent in charge of the pharmacy to assure its integrity when a registered pharmacist is not physically present, but may not perform any duties which require the exercise of the pharmacist’s independent professional judgment. The technician may not be left in charge for more than 30 minutes; and
(h) compounding if a mechanism for verification by the supervising pharmacist exists that includes checking of: the original order; additives; dosages; and clarity of IV solution, where appropriate.
(2) The board reserves the right to evaluate and amend the functions allowable by a pharmacy technician, with final determination in the sole discretion of the board.
History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-7-101, 37-7-201, 37-7-301, 37-7-307, MCA; NEW, 1992 MAR p. 1608, Eff. 7/31/92; AMD, 2002 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; TRANS, from Commerce, 2002 MAR p. 904; AMD, 2006 MAR p. 1615, Eff. 6/23/06.
24.174.713 CONTENTS OF TRAINING COURSE
(1) A pharmacy technician training course must include instruction in:
(a) orientation to the practice of pharmacy;
(b) pharmacy terminology and basic pharmaceutics;
(c) state and federal laws relating to the practice of pharmacy;
(d) pharmaceutical calculations;
(e) processing prescription drug orders;
(f) telephone procedure and communication including taking refill requests;
(g) pharmaceutical compounding;
(h) intravenous admixture, if applicable; and
(i) use of pharmacy computer systems, if applicable.
History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-7-201, 37-7-307, MCA; NEW, 1992 MAR p. 1608, Eff. 7/31/92; AMD, 2002 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; TRANS, from Commerce, 2002 MAR p. 904.
24.174.715 TECHNICIAN CHECK TECHNICIAN PROGRAM
(1) To participate in a technician check technician (TCT) program an institutional pharmacy within a hospital must meet the following requirements:
(a) the pharmacy must include TCT as a technician duty, submitted to the Board of Pharmacy by the pharmacist-in-charge as part of the technician utilization plan;
(b) develop a site-specific training program tailored to the patient population and medication distribution system;
(c) designate one pharmacist to be responsible for meeting the TCT program training and validation requirements;
(d) staffing must be adequate to support a consistent utilization of the TCT program;
(e) a pharmacist must review all orders against a medication profile containing pertinent clinical information about the patient (allergies, current medication, etc.);
(f) the medication description on the batch fill list must contain the same description as the labeling on the unit dose package;
(g) the drug distribution system must be structured so that at least one additional check of dispensed medications is completed prior to administration;
(h) develop policies and procedures which include a list of the types of work that a technician may check and the types of work that are excluded from being checked by a technician; and
(i) utilize the TCT program as a tool to redirect pharmacists from distributive tasks to cognitive and patient centered activities.
(2) In order to participate in a TCT program a technician must:
(a) be a registered pharmacy intern in good standing with the board with at least three months experience in unit dose filling; or
(b) be a certified pharmacy technician in good standing with the board working full or part time with six months equivalent experience in unit dose filling; and
(c) complete site specific training in the TCT program.
(3) A TCT training program must include:
(a) didactic lecture (or equivalent training with a self-learning packet);
(b) practical sessions (one-on-one training) which consist of observation of a pharmacist checking a unit dose medication batch and/or cart;
(c) initial validation (and revalidation if needed); and
(d) regular quality assurance audits performed quarterly for the first year then every six months thereafter.
(4) Approval from the Board of Pharmacy or designee is required prior to program implementation.
(5) If at any time a technician loses their validation, that individual must not function as a TCT until they are retrained and revalidated.
(6) All TCT program materials should be readily retrievable for review by the board inspector.
(7) Any facility that is not within an institutional pharmacy within a hospital must come before the board.
History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-7-101, 37-7-201, 37-7-301, 37-7-307, MCA; NEW, 2007 MAR p. 1936, Eff. 11/22/07.
24.174.2102 PHARMACY TECHNICIAN – RENEWAL
(1) Pharmacy technicians will be required to renew each year on the date set forth in ARM 24.101.413.
(2) To assure the continuing competence of a pharmacy technician, in order to renew a license, the pharmacy technician must be in compliance with all certification requirements at the time of renewal. (History: 37-7-201, MCA; IMP, 37-1-141, 37-7-201, MCA; NEW, 2002 MAR p. 86, Eff. 1/18/02; AMD, 2010 MAR p. 74, Eff. 1/15/10.)
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives