
Second Academic Year for Medication Safety Scholars Program
March 22, 2024
Really excited to share the news that we will be beginning the second academic year for the Emily Jerry Foundation‘s Medication Safety Scholars Program! This comprehensive distance education and virtual engagement program was developed and successfully implemented over the… Read More



New Mexico Scorecard
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
New Mexico Law
I. Laws
New Mexico Drug and Pharmacy Statutes
http://www.conwaygreene.com/nmsu/lpext.dll?f=templates&fn=main-h.htm&2.0
61-11-1.1. Legislative findings; purpose of act. (Repealed effective July 1, 2016.)
A. The legislature finds that the practice of pharmacy in New Mexico is a professional practice affecting the public health, safety and welfare and is subject to regulation and control in the public interest. The legislature finds further that it is a matter of public interest and concern that the practice of pharmacy as defined in the Pharmacy Act merit and receive the confidence of the public, and that only qualified persons be permitted to engage in the practice of pharmacy so that the quality of drugs and related devices distributed in New Mexico is ensured.
B. The purpose of the Pharmacy Act is to promote, preserve and protect the public health, safety and welfare by and through the effective control and regulation of the practice of pharmacy, including the licensure of pharmacists and pharmacist interns and registration of pharmacy technicians; the licensure, control and regulation of all sites or persons, in or out of state, who distribute, manufacture or sell drugs or devices used in the dispensing and administration of drugs in New Mexico; and the regulation and control of such other materials as may be used in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of injury, illness or disease of a patient or other person.
61-11-6. Powers and duties of board. (Repealed effective July 1, 2016.)
A. The board shall:
(1) adopt, amend or repeal rules and regulations necessary to carry out the provisions of the Pharmacy Act in accordance with the provisions of the Uniform Licensing Act [61-1-1 NMSA 1978];
(2) provide for examinations of applicants for licensure as pharmacists;
(3) provide for the issuance and renewal of licenses for pharmacists;
(4) require and establish criteria for continuing education as a condition of renewal of licensure for pharmacists;
(5) provide for the issuance and renewal of licenses for pharmacist interns and for their training, supervision and discipline;
(6) provide for the licensing of retail pharmacies, nonresident pharmacies, wholesale drug distributors, drug manufacturers, hospital pharmacies, nursing home drug facilities, industrial and public health clinics and all places where dangerous drugs are stored, distributed, dispensed or administered and provide for the inspection of the facilities and activities;
(7) enforce the provisions of all laws of the state pertaining to the practice of pharmacy and the manufacture, production, sale or distribution of drugs or cosmetics and their standards of strength and purity;
(8) conduct hearings upon charges relating to the discipline of a registrant or licensee or the denial, suspension or revocation of a registration or a license in accordance with the Uniform Licensing Act;
(9) cause the prosecution of any person violating the Pharmacy Act, the New Mexico Drug, Device and Cosmetic Act [26-1-1 NMSA 1978] or the Controlled Substances Act [30-31-1 NMSA 1978];
(10) keep a record of all proceedings of the board;
(11) make an annual report to the governor;
(12) appoint and employ, in the board’s discretion, a qualified person who is not a member of the board to serve as executive director and define the executive director’s duties and responsibilities; except that the power to deny, revoke or suspend any license or registration authorized by the Pharmacy Act shall not be delegated by the board;
(13) appoint and employ inspectors necessary to enforce the provisions of all acts under the administration of the board, which inspectors shall be pharmacists and have all the powers and duties of peace officers;
(14) provide for other qualified employees necessary to carry out the provisions of the Pharmacy Act;
(15) have the authority to employ a competent attorney to give advice and counsel in regard to any matter connected with the duties of the board, to represent the board in any legal proceedings and to aid in the enforcement of the laws in relation to the pharmacy profession and to fix the compensation to be paid to the attorney; provided, however, that the attorney shall be compensated from the money of the board, including that provided for in Section 61-11-19 NMSA 1978;
(16) register and regulate qualifications, training and permissible activities of pharmacy technicians;
(17) provide a registry of all persons licensed as pharmacists or pharmacist interns in the state;
(18) adopt rules and regulations that prescribe the activities and duties of pharmacy owners and pharmacists in the provision of pharmaceutical care, emergency prescription dispensing, drug regimen review and patient counseling in each practice setting;
(19) adopt, after approval by the New Mexico board of medical examiners and the board of nursing, rules and protocols for the prescribing of dangerous drug therapy, including vaccines and immunizations, and the appropriate notification of the primary or appropriate physician of the person receiving the dangerous drug therapy; and
(20) have the authority to authorize emergency prescription dispensing.
B. The board may:
(1) delegate its authority to the executive director to issue temporary licenses as provided in Section 61-11-14 NMSA 1978;
(2) provide by regulation for the electronic transmission of prescriptions; and
(3) delegate its authority to the executive director to authorize emergency prescription dispensing procedures during civil or public health emergencies.
History: 1953 Comp., § 67-9-37, enacted by Laws 1969, ch. 29, § 5; 1972, ch. 84, § 55; 1977, ch. 62, § 1; 1979, ch. 293, § 1; 1983, ch. 165, § 1; 1992, ch. 19, § 2; 1997, ch. 131, § 6; 2001, ch. 50, § 4; 2005, ch. 152, § 5.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
61-11-11.1. Pharmacy technician; qualifications; duties. (Repealed effective July 1, 2016.)
A. The classification of pharmacy technician is established. An applicant for registration as a pharmacy technician shall:
(1) be at least eighteen years of age and not addicted to drugs or alcohol;
(2) complete initial training as required by regulations of the board that includes on-the-job and related education commensurate with the tasks to be performed by the pharmacy technician; and
(3) if the potential duties of the pharmacy technician will include the preparation of sterile products, complete an additional one hundred hours of experiential training as required by regulations of the board.
B. Permissible activities for pharmacy technicians under the supervision of a pharmacist include:
(1) the preparation, mixing, assembling, packaging and labeling of medications;
(2) processing routine orders of stock supplies;
(3) preparation of sterile products;
(4) filling of a prescription or medication order that entails counting, pouring, labeling or reconstituting medications; and
(5) tasks assigned by the supervising pharmacist that do not require his professional judgment.
C. The supervising pharmacist shall observe and direct the pharmacy technician to a sufficient degree to assure the accurate completion of the activities of the pharmacy technician and shall provide a final check of all aspects of the prepared product and document the final check before dispensing.
D. The supervising pharmacist shall be responsible for the tasks performed by the pharmacist technician and subject to discipline for failure to appropriately supervise the performance of the pharmacist technician.
History: Laws 1997, ch. 131, § 12; 2005, ch. 152, § 7.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
61-11-12. License fees. (Repealed effective July 1, 2016.)
A. An applicant for licensure as a pharmacist or pharmacist intern or registration as a pharmacy technician shall pay the following fees, which fees shall not be returnable:
(1) for initial licensure as a pharmacist, a fee set by the board not to exceed four hundred dollars ($400); provided that if the applicant fails a portion of an examination, reexamination is subject to the same fee as the first examination;
(2) for initial licensure as a pharmacist intern, a fee not to exceed twenty-five dollars ($25.00); and
(3) for initial registration as a pharmacy technician, a fee not to exceed twenty-five dollars ($25.00).
B. The board shall issue a license or registration to each successful applicant and enter his name and pertinent information in the registry maintained by the board.
C. Every registration or license shall have the seal of the board affixed and be signed by the board chairman.
History: 1953 Comp., § 67-9-43, enacted by Laws 1969, ch. 29, § 11; 1972, ch. 43, § 1; 1983, ch. 165, § 2; 1989, ch. 103, § 1; 1997, ch. 131, § 13.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
New Mexico Administrative Code
http://www.nmcpr.state.nm.us/nmac/_title16/T16C019.htm
TITLE 16 OCCUPATIONAL AND PROFESSIONAL LICENSING
CHAPTER 19 PHARMACISTS
PART 22 SUPPORT PERSONNEL AND PHARMACY TECHNICIANS
16.19.22.1 ISSUING AGENCY: Regulation and Licensing Department-Board of Pharmacy, (505) 222-9835.
[16.19.22.1 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.1, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10]
16.19.22.2 SCOPE: All Pharmacy technicians and non-technicians supportive personnel, supervising pharmacists and pharmacists in charge of entities that utilize supportive personnel.
[16.19.22.2 NMAC – Rp, 16. NMAC 19.22.2, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.3 STATUTORY AUTHORITY: Section 61-11-6-(A) NMSA 1978 authorizes the Board of pharmacy to register and regulate qualifications, training and permissible activities of pharmacy technicians.
[16.19.22.3 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.3, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.4 DURATION: Permanent.
[16.19.22.4 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.4, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.5 EFFECTIVE DATE: June 27, 2001, unless a later date is cited at the end of a section.
[16.19.22.5 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.5, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.6 OBJECTIVE: The objective of Part 22 of Chapter 19 is to promote responsive delivery of pharmaceutical products and services to the public by establishing standards for training and supervision of support personnel and limitations on their use.
[16.19.22.6 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.6, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.7 DEFINITIONS:
A. “Direct supervision” means that the pharmacist onsite shall observe and direct to a degree sufficient to assure the accurate completion of the activities of the pharmacy technicians and must provide a final check of all aspects of the prepared product and document the final check before dispensing.
B. “Indirect supervision” means that the pharmacist offsite shall observe via live surveillance cameras and direct pharmacy activity remotely via remote tele-pharmacy communication technology to a degree sufficient to assure the accurate completion of the activities of the pharmacy technicians and must provide a final check of all aspects of the prepared product and document the final check before dispensing.
C. “Pharmacy technician” means a person who, under the supervision of a licensed pharmacist, performs repetitive tasks not requiring the professional judgment of a pharmacist. This includes assisting in various technical activities associated with the preparation and distribution of medications.
(1) “Certified pharmacy technician” means a pharmacy technician who has completed the training and certification outlined in 16.19.22.9 NMAC, completed a board approved certification exam, is registered by the board of pharmacy and maintains current board approved certification.
(2) “Non-certified pharmacy technician” means a pharmacy technician who is in the process of completing the training and education outlined in 16.19.22.9 NMAC and is registered by the board of pharmacy.
(3) “Remote pharmacy technician” means a certified pharmacy technician who meets the special requirements for indirect supervision at a remote dispensing site as specified in the board of pharmacy tele-pharmacy regulations.
D. “Prescription drug” means and human drug required by federal or state law or regulation to be dispensed only by a prescription, including finished dosage forms and active ingredients subject to Section 503(b) of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act.
E. “Professional judgment” means a cognitive process, by a licensed professional, that takes education, experience, current primary literature and current standards of practice into consideration when drawing conclusions and reaching decisions.
F. “Stocking” means placement of the prescription drug container on the pharmacy shelf.
G. “Supervision” means that the pharmacist shall observe and direct to a sufficient degree to assure the accurate completion of the activities of the pharmacy technicians and must provide a final check of all aspects of the prepared product and document the final check before dispensing.
H. “Support personnel” means pharmacy personnel other than pharmacy technicians, which may include clerks, secretary’s and delivery personnel, who under the supervision of a pharmacist, may perform duties associated with the practice of pharmacy, excluding the direct processing and filling of prescriptions, stocking prescription drugs, or duties restricted to only a pharmacist, pharmacist intern, or pharmacy technician.
I. “Technician training sponsor” means pharmacist-in-charge, pharmacist or designated administrator at a pharmacy technician training program who assumes responsibility for training and duties performed by a non-certified technician.
[16.19.22.7 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.7, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10; A, 11-27-11]
16.19.22.8 PERMISSIBLE ACTIVITIES: Pharmacy technician activities under the direct supervision of a pharmacist shall be limited to tasks enumerated in policies and procedures implemented by the pharmacist-in-charge that do not require professional judgment.
[16.19.22.8 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.8, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10]
16.19.22.9 TRAINING AND EDUCATION:
A. The pharmacist-in-charge shall ensure that the pharmacy technician has completed initial training which includes:
(1) federal and state laws and regulations that affect pharmacy practice; specific regulations which address the use of supportive personnel and technicians;
(2) ethical and professional standards of practice;
(3) medical and pharmaceutical terminology, symbols and abbreviations used in the practice of pharmacy and components of a prescription;
(4) pharmaceutical calculations necessary for the preparation and dispensing of drug products;
(5) manufacturing, preparation, packaging, labeling and proper storage of drug products;
(6) dosage forms and routes of administration; and
(7) trade and generic names for medications frequently dispensed by the pharmacy;
(8) basic comprehension of pharmacology;
(9) basic knowledge of appropriate pharmacy references.
B. If the duties of the technician will include the preparation of sterile products then, in addition to the training and education requirements listed in this section, the technician will complete training outlined in Paragraph (2) of Subsection C of 16.19.6.11 NMAC.
C. A written record of training and education will be maintained by the pharmacy technician and contain the following:
(1) name of person receiving the training;
(2) date(s) of the training;
(3) description of the topics covered;
(4) names of the person(s) who provided the training; and
(5) signature of the technician and the technician training sponsor.
D. A written record of training and education must be submitted to the board with certification exam documentation to obtain certified pharmacy technician registration.
E. All technicians are required to obtain board approved certification within one year of registration with the board as a technician. Extensions will no longer be granted to pharmacy technicians registered on or after November 15, 2010.
F. The pharmacist-in-charge shall be responsible for the implementation of policies and procedures for additional training appropriate to duties and responsibilities performed by a pharmacy technician as well as an ongoing quality assurance plan to assure competency.
[16.19.22.9 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.9, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10; A, 11-27-11]
16.19.22.10 RATIO OF TECHNICIANS TO PHARMACISTS:
A. The permissible ratio of pharmacy technicians to pharmacists on duty is 4-1. Support personnel are not included in this ratio.
B. The ratio may be increased if the pharmacy submits to the Board of Pharmacy a protocol for increased ratios and the Board approves the protocol.
[16.19.22.10 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.10, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.11 IMPROPER ACTIVITIES OF PHARMACY TECHNICIANS:
A. The supervising pharmacist and the pharmacist-in-charge are responsible for the actions of pharmacy technicians. Performance of tasks by the pharmacy technician and support personnel outside the limits of the regulations that are authorized by the supervising pharmacist shall constitute unprofessional conduct on the part of the pharmacist and the pharmacist-in-charge.
(1) The following responsibilities require the use of professional judgment and therefore shall be performed only by a pharmacist or pharmacist intern:
(a) receipt of all new verbal prescription orders and reduction to writing;
(b) evaluation and interpretation of the prescription order and any necessary clinical clarification prior to dispensing;
(c) clinical consultation with a patient or his agent regarding a prescription or over-the-counter drug;
(d) evaluation of available clinical data in patient medication record system;
(e) oral communication with the patient or patient’s agent of information, as defined in the section under patient counseling, in order to improve therapy by ensuring proper use of drugs and devices;
(f) professional consultation with the prescriber, the prescriber’s agent, or any other health care professional or authorized agent regarding a patient and any medical information pertaining to the prescription.
(2) ONLY A PHARMACIST SHALL PERFORM THE FOLLOWING DUTIES:
(a) final check on all aspects of the completed prescription including sterile products and cytotoxic preparations, and assumption of the responsibility for the filled prescription, including, but not limited to, appropriateness of dose, accuracy of drug, strength, labeling, verification of ingredients and proper container;
(b) evaluation of pharmaceuticals for formulary selection within the facility;
(c) supervision of all pharmacy technicians and support personnel activities including preparations, mixing, assembling, packaging, labeling and storage of medication;
(d) ensure the pharmacy technicians and support personnel have been properly trained for the duties they may perform;
(e) any verbal communication with a patient or patient’s representative regarding a change in drug therapy or performing therapeutic interchanges (i.e. drugs with similar effects in specific therapeutic categories); this does not apply to substitution of generic equivalents;
(f) any other duty required of a pharmacist by any federal or state law.
B. In accordance with section 61-11-20 NMSA 1978 a pharmacy technicians registration may be revoked, denied, or suspended for grounds stated in section 61-11-20(A).
[16.19.22.11 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.11, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10]
16.19.22.12 IDENTIFICATION OF PHARMACY PERSONNEL: All personnel in pharmacy restricted area shall wear an identification badge which must include name and job title.
[16.19.22.12 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.12, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.13 (RESERVED)
[16.19.22.13 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.13, 06-27-2001]
16.19.22.14 REGISTRATION OF PHARMACY TECHNICIANS:
A. Application (and required registration fee) shall be submitted to the board prior to performing any technician duties. Non-certified pharmacy technicians must:
(1) Complete requirements for certified pharmacy technician within (1) one year of original application.
(2) Not re-apply with the board of pharmacy as a non-certified pharmacy technician.
(3) Provide the name of the technician training sponsor responsible for training and education with application.
(4) Provide documentation of training and completion of certification exam to be registered as a certified pharmacy technician.
B. Registration for certified pharmacy technicians will expire biennially on the last day of their birth month and must be renewed prior to expiration. Registration renewal applications must include documentation of current national certification.
[16.19.22.14 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.14, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10]
16.19.22.15 CHANGE OF ADDRESS: Pharmacy technicians shall report in writing or through the online process available on the board’s website of any change of address or employment to the board within ten (10) days.
[16.19.22.15 NMAC – Rp, 16 NMAC 19.22.15, 06-27-2001; A, 11-15-10]
HISTORY of 16.19.22 NMAC:
Pre-NMAC History:
Regulation 22, Supportive Personnel, filed 01/29/93.
History of Repealed Material:
16 NMAC 19.22, Supportive Personnel, filed 02/02/96.
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
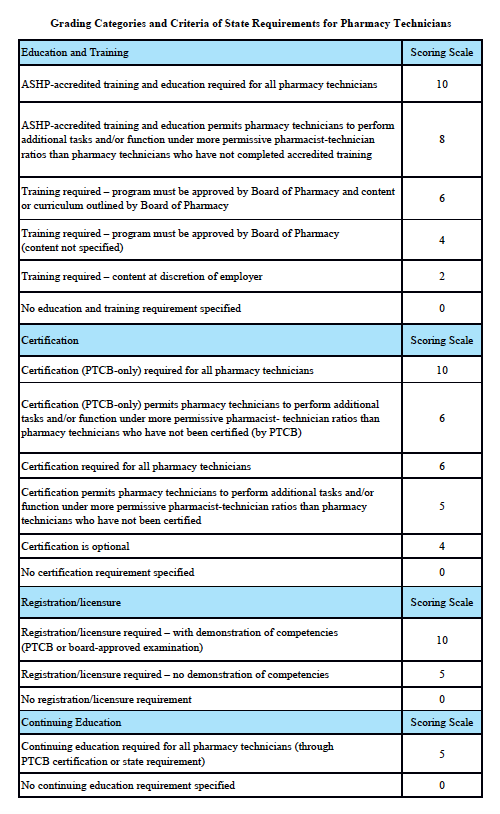
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives