(4) Upon the declaration of a national, state, or local emergency, a public health emergency as defined in Section 26B-7-301, or a declaration by the president of the United States or other federal official requesting public health-related activities, the division in collaboration with the relevant board may:
(b) modify, under the circumstances described in this Subsection (4) and Subsection (5), the scope of practice restrictions under this title for individuals who are licensed under this title as: (iv) a pharmacist, pharmacy technician, or pharmacy intern under Chapter 17b, Pharmacy Practice Act;” “58-17b-102. Definitions. (33) “Licensed pharmacy technician” means an individual licensed with the division, that may, under the supervision of a pharmacist, perform the activities involved in the technician practice of pharmacy. (55) “Pharmacy technician training program” means an approved technician training program providing education for pharmacy technicians. (57) (a) “Practice as a licensed pharmacy technician” means engaging in practice as a pharmacy technician under the general supervision of a licensed pharmacist and in accordance with a scope of practice defined by division rule made in collaboration with the board. (b) “Practice as a licensed pharmacy technician” does not include: (i) performing a drug utilization review, prescription drug order clarification from a prescriber, final review of the prescription and prescribed drug prepared for dispensing, dispensing of the drug, or counseling a patient with respect to a prescription drug; (ii) counseling regarding nonprescription drugs and dietary supplements unless delegated by the supervising pharmacist; or (iii) receiving new prescription drug orders when communicating telephonically or electronically unless the original information is recorded so the pharmacist may review the prescription drug order as transmitted. (72) “Supportive personnel” means unlicensed individuals who: (a) may assist a pharmacist, pharmacist preceptor, pharmacy intern, or licensed pharmacy technician in nonjudgmental duties not included in the definition of the practice of pharmacy, practice of a pharmacy intern, or practice of a licensed pharmacy technician, and as those duties may be further defined by division rule adopted in collaboration with the board; and (b) are supervised by a pharmacist in accordance with rules adopted by the division in collaboration with the board.
58-17b-301. License required – License classifications for individuals. (1) A license is required to engage in the practice of pharmacy, telepharmacy, or the practice of a pharmacy technician, or dispensing medical practitioner except as specifically provided in Section 58-1-307 or 58-17b-309. (2) The division shall issue to an individual who qualifies under this chapter a license in the classification of: (a) pharmacist; (b) pharmacy intern; or (c) pharmacy technician; (d) dispensing medical practitioner; or (e) pharmacy technician trainee.” “58-17b-305. Qualifications for licensure of pharmacy technician. (1) An applicant for licensure as a pharmacy technician shall: (a) submit an application in a form prescribed by the division the division approves; (b) pay a fee determined by the department under Section 63J-1- 504; (c) (i) consent to, and complete, a criminal background check, described in Section 58-1-301.5; (ii) meet any other standard related to the criminal background check described in Subsection (1)(c)(i), that the division establishes by rule in accordance with Title 63G, Chapter 3, Utah Administrative Rulemaking Act; and (iii) disclose any criminal history the division requests on a form the division approves; (d) have no physical or mental condition of a nature that prevents the applicant from engaging in practice as a pharmacy technician with reasonable skill, competency, and safety to the public; (e) have completed a program and curriculum of education and training, meeting standards established by division rule made in collaboration with the board; and (f) successfully complete the examinations requirement within the time periods established by division rule made in collaboration with the board. (2) A pharmacist whose license has been denied, revoked, suspended, or restricted for disciplinary purposes is not eligible to be a licensed pharmacy technician while on probation with the division.
R156-17b-102. Definitions. (29) “ExCPT”, as used in this rule, means the Exam for the Certification of Pharmacy Technicians. (53) “PTCB” means the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board.
R156-17b-303a. Qualifications for Licensure – Pharmacist, Pharmacy Intern, and Pharmacy Technician – Education Requirements. (1) Under Subsections 58-17b-303(2) and 58-17b-304(6)(b), the credentialing agency recognized to provide certification and evaluate equivalency of a foreign educated pharmacy graduate is the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Examination Committee (FPGEC) of the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy. (2) Under Subsection 58-17b-304(6), an applicant for a pharmacy intern license shall: (a) be a current pharmacy student in a college of pharmacy accredited by the ACPE, as evidenced by written verification from a dean of the college; (b) hold a graduate degree from a foreign pharmacy school and have received a certificate of equivalency from an approved credentialing agency under Subsection (1); or (c) have been accepted to a college of pharmacy accredited by the ACPE, as evidenced by a written acceptance letter from the college of pharmacy showing that the applicant is expected to begin coursework in the college of pharmacy no more than 90 days from the date of the application. (3) Under Subsection 58-17b-305(1)(e), a pharmacy technician shall complete a training program that: (a) is accredited by: (i) ASHP; or (ii) the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES); or (b) is conducted by: (i) a program approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board; or (ii) a branch of the Armed Forces of the United States; and (c) meets the following standards: (i) requires completion, while licensed as a pharmacy technician trainee, of at least 180 hours of directly supervised practical training in a licensed pharmacy by a licensed pharmacist in good standing; and (ii) has written protocols and guidelines for the teaching pharmacist outlining the use and supervision of pharmacy technician trainees that address: (A) the specific manner in which supervision will be completed; and (B) an evaluative procedure to verify the accuracy and completeness of any act, task, and function performed by the pharmacy technician trainee. (4) A pharmacy technician trainee shall complete a pharmacy technician training program and pass the required examination in Subsection R156-17b-303c(4) within two years after obtaining their pharmacy technician trainee license, unless otherwise approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board for good cause showing exceptional circumstances. An individual who fails to comply with this time frame shall repeat a pharmacy technician training program in its entirety if the individual pursues licensure as a pharmacy technician. (5)(a) A Division approved program or program in ASHP candidate status shall notify a student before enrollment that if the program is denied accreditation status while the student is enrolled in the program, the student will be required to complete education in another program with no assurance of how many credits will transfer to the new program. (b) A Division approved program or program in ASHP candidate status that is denied accreditation shall immediately notify the Division, enrolled students, and student practice sites, of the denial. (c) The notice required in Subsection (5)(b) shall instruct each student and practice site that:(i) the program no longer satisfies the pharmacy technician license education requirement in Utah; and(ii) enrollment in a different program meeting requirements in Subsection R156-17b-303a(3) is necessary for the student to complete training and to satisfy the pharmacy technician license education requirement in Utah. (6) An applicant from another jurisdiction seeking licensure as a pharmacy technician in Utah who does not meet the qualifications for licensure by endorsement in Subsection 58-1-302(2), meets the qualifications for licensure in Subsections 58-1-302(3), 58-17b-305(1)(e), and 58-17b-305(1)(f) if the applicant: (a)(i) has engaged in the practice of a pharmacy technician for a minimum of 1,000 hours in that jurisdiction within the past two years; or (ii) has equivalent experience as approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board; and (b) has current PTCB or ExCPT certification.” “R156-17b-302. Licensure – Examinations. is now R156-17b-303c. Change to the following verbiage:
R156-17b-303c. Qualifications for Licensure – Pharmacist and Pharmacy Technician – Examinations. (1) An applicant seeking licensure as a pharmacist under Subsection 58-17b-303(1), shall pass the following examinations within five years of graduation from a pharmacy program described in Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(e): (a) the NAPLEX with a passing score established by NABP; and (b) the Utah MPJE with a passing score established by NABP. (2) An applicant seeking licensure as a pharmacist by endorsement under Subsection 58-17b-303(3), shall pass the Utah MPJE, with a passing score established by NABP. (3) An applicant under Subsection 58-17b-303(1) or Subsection 58-17b-303(3) who has failed a required examination three times and wishes to retake the exam shall: (a) meet with the Board to request authorization to test up to two additional attempts; and (b) complete any additional training the Board may require before any approved additional attempts. (4) An applicant under Subsection 58-17b-303(1) or Subsection 58-17b-303(3) who has failed a required examination five times and who wishes to retake the exam shall complete another education program in accordance with Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(e) before an additional authorization to test. (5) An applicant shall pass any required examination within five years of graduation from an education program in accordance with Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(e). (6)(a) Under Subsection 58-17b-305(1)(f), an applicant for licensure as a pharmacy technician shall pass the PTCB or ExCPT with a passing score established by the certifying body.(b) A PTCB or ExCPT certificate shall show a valid date and that the certification is active. (7) In addition to any applicable examination requirements of Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(g) or Subsection 58-17b-303(3)(i), a graduate of a foreign pharmacy school seeking licensure under Subsection 58-17b-303(2) shall obtain a passing score on the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Examination Committee (FPGEC) examination.
R156-17b-309. Continuing Education. Under Section 58-17b-310 and Subsections 58-1-203(1)(g) and 58-1-308(3)(b), this section establishes the continuing education (CE) requirements for renewal or reinstatement of a pharmacist or pharmacy technician license for each two-year renewal cycle. (1) A pharmacist shall complete at least 30 CE hours which shall: (a) include 12 hours of live or technology-enabled participation in lectures, seminars, or workshops; (b) be relevant to the licensee’s professional practice; (c) include one hour of pharmacy law or ethics; (d) if engaging in the administration of vaccines under Section R156-17b-621, include two hours in vaccine-related topics; (e) if engaging in the administration of prescription drugs or devices under Section R156-17b-621 or R156-17b-625, include two hours in topics related to the administration of those prescription drugs or devices; and (f) if dispensing a self-administered hormonal contraceptive in accordance with Title 26B, Chapter 4, Family Planning Access Act under Section R156-17b-621b, include two hours in topics related to hormonal contraceptive therapy.(2)(a) A pharmacy technician shall complete at least 20 CE hours, which shall include:(i) six hours of live or technology-enabled participation at lectures, seminars, or workshops;(ii) one hour of pharmacy law or ethics; and(iii) if engaging in the administration of vaccines under Section R156-17b-621, two hours in vaccine-related topics.(b) Current PTCB or ExCPT certification shall fulfill each CE requirements for a pharmacy technician, except for vaccine-related topic hours that may be required under Subsection (2)(a)(iii).(3)(a) If a licensee first becomes licensed during the two-year renewal cycle, the licensee’s required number of CE hours shall be decreased proportionately according to the date of licensure.(b) The Division may defer or waive each CE requirements as provided in Section R156-1-308d.(4) CE credit shall be recognized as follows:(a)(i) one live CE hour for attending one Board of Pharmacy meeting, up to a maximum of two CE hours during each two-year period; and(ii) these hours may count as “”pharmacy law or ethics”” hours;(b)(i) two CE hours for each hour of lecturing or instructing a CE course or teaching in the licensee’s profession, up to a maximum of ten CE hours during each two-year period;(ii) the licensee shall document the course’s content and intended audience such as pharmacists, pharmacy technicians, pharmacy interns, physicians, or nurses; and(iii) public service programs, such as presentations to schoolchildren or service clubs, are not eligible for CE credit; and(c) CE credit shall be approved by, conducted by, or under the sponsorship of one of the following:(i) institutes, seminars, lectures, conferences, workshops, various forms of mediated instruction, and programmed learning courses, presented by an ACPE-approved institution, individual, organization, association, corporation, or agency;(ii) programs approved by health-related CE approval organizations, if the CE is nationally recognized by a healthcare accrediting agency and is related to the practice of pharmacy;(iii) Division training or educational presentations;(iv) educational meetings that are ACPE accredited and are sponsored by the Utah Pharmacy Association, the Utah Society of Health-System Pharmacists, or other professional organization or association; or(v) for pharmacists, programs of certification by qualified individuals such as certified diabetes educator credentials, board certification, or other certification as approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board.(5) A licensee shall maintain documentation sufficient to prove compliance with this section, for a period of four years after the end of the renewal cycle for which the CE is due, by:(a) maintaining registration with the NABP e-Profile CPE Monitor plan or the NABP CPE Monitor Plus plan; and(b) maintaining a certificate of completion or other adequate documentation for CE that cannot be tracked by the licensee’s NABP plan.
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
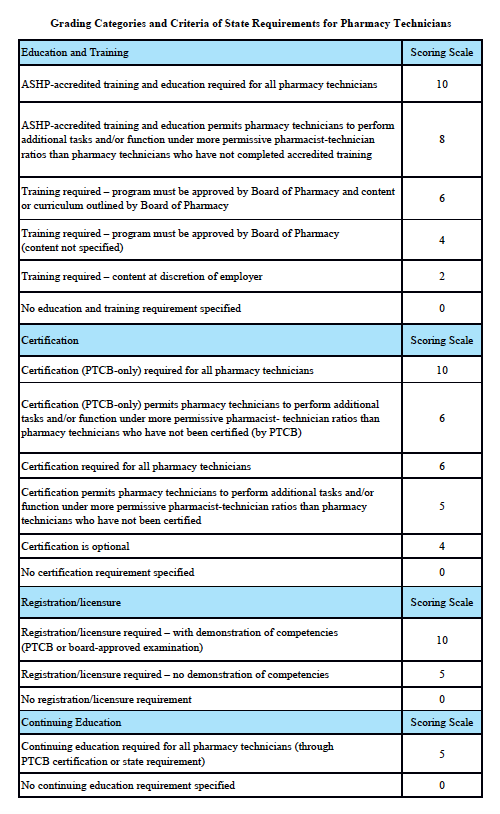
Scoring rationale for Education and Training: In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification: Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure: Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education: Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s,
world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with
our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important
objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient
safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that
are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine.
Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working
hard to save lives every day.
Tomorrow, I’m really looking forward to heading to Monterey, California to speak on behalf of the Emily Jerry Foundation at the Pacific Coast Patient Safety Conference, hosted by the California Society of Health – System Pharmacists. But today… Read More
The week before last truly meant a great deal to me. I was honored to be invited back to Touro College of Pharmacy to deliver another Dean’s Hour lecture, after having the privilege of speaking there last April…. Read More
I’m really looking forward to heading to New York City this morning for two very meaningful speaking engagements at Touro University’s College of Pharmacy. This journey began with an invitation to deliver a CE presentation at the NYCSHP… Read More
Utah Scorecard
Grading Scale:
A – 85-100%, B – 70-84.9%, C – 55-69.9%, D – 40-54.9%, F – 0-39.9%
Grading Categories & Criteria
Utah Law
I. Laws
UTAH STATUTES
https://le.utah.gov/xcode/Title58/Chapter17b/58-17b.html
58-1-307 Exemptions from licensure
(4) Upon the declaration of a national, state, or local emergency, a public health emergency as defined in Section 26B-7-301, or a declaration by the president of the United States or other federal official requesting public health-related activities, the division in collaboration with the relevant board may:
(b) modify, under the circumstances described in this Subsection (4) and Subsection (5), the scope of practice restrictions under this title for individuals who are licensed under this title as:
(iv) a pharmacist, pharmacy technician, or pharmacy intern under Chapter 17b, Pharmacy Practice Act;” “58-17b-102. Definitions.
(33) “Licensed pharmacy technician” means an individual licensed with
the division, that may, under the supervision of a pharmacist,
perform the activities involved in the technician practice of
pharmacy.
(55) “Pharmacy technician training program” means an approved
technician training program providing education for pharmacy
technicians.
(57) (a) “Practice as a licensed pharmacy technician” means engaging
in practice as a pharmacy technician under the general
supervision of a licensed pharmacist and in accordance with
a scope of practice defined by division rule made in
collaboration with the board.
(b) “Practice as a licensed pharmacy technician” does not
include:
(i) performing a drug utilization review, prescription
drug order clarification from a prescriber, final
review of the prescription and prescribed drug
prepared for dispensing, dispensing of the drug, or
counseling a patient with respect to a prescription
drug;
(ii) counseling regarding nonprescription drugs and
dietary supplements unless delegated by the
supervising pharmacist; or
(iii) receiving new prescription drug orders when
communicating telephonically or electronically unless
the original information is recorded so the
pharmacist may review the prescription drug order as
transmitted.
(72) “Supportive personnel” means unlicensed individuals who:
(a) may assist a pharmacist, pharmacist preceptor, pharmacy
intern, or licensed pharmacy technician in nonjudgmental
duties not included in the definition of the practice of
pharmacy, practice of a pharmacy intern, or practice of a
licensed pharmacy technician, and as those duties may be
further defined by division rule adopted in collaboration
with the board; and
(b) are supervised by a pharmacist in accordance with rules
adopted by the division in collaboration with the board.
58-17b-301. License required – License classifications for individuals.
(1) A license is required to engage in the practice of pharmacy,
telepharmacy, or the practice of a pharmacy technician, or dispensing medical practitioner except as
specifically provided in Section 58-1-307 or 58-17b-309.
(2) The division shall issue to an individual who qualifies under
this chapter a license in the classification of:
(a) pharmacist;
(b) pharmacy intern; or
(c) pharmacy technician;
(d) dispensing medical practitioner; or
(e) pharmacy technician trainee.” “58-17b-305. Qualifications for licensure of pharmacy technician.
(1) An applicant for licensure as a pharmacy technician shall:
(a) submit an application in a form prescribed by the division the division approves;
(b) pay a fee determined by the department under Section 63J-1-
504;
(c)
(i) consent to, and complete, a criminal background check, described in Section 58-1-301.5;
(ii) meet any other standard related to the criminal background check described in Subsection (1)(c)(i), that the division establishes by rule in accordance with Title 63G, Chapter 3, Utah Administrative Rulemaking Act; and
(iii) disclose any criminal history the division requests on a form the division approves;
(d) have no physical or mental condition of a nature that prevents the applicant from engaging in practice as a pharmacy technician with reasonable skill, competency, and safety to the public;
(e) have completed a program and curriculum of education and training, meeting standards established by division rule made in collaboration with the board; and
(f) successfully complete the examinations requirement within the time periods established by division rule made in collaboration with the board.
(2) A pharmacist whose license has been denied, revoked, suspended,
or restricted for disciplinary purposes is not eligible to be a
licensed pharmacy technician while on probation with the
division.
Utah Rules
https://adminrules.utah.gov/public/rule/R156-17b/Current%20Rules
R156-17b-102. Definitions.
(29) “ExCPT”, as used in this rule, means the Exam for the Certification of
Pharmacy Technicians.
(53) “PTCB” means the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board.
R156-17b-303a. Qualifications for Licensure – Pharmacist, Pharmacy Intern, and Pharmacy Technician – Education Requirements.
(1) Under Subsections 58-17b-303(2) and 58-17b-304(6)(b), the credentialing agency recognized to provide certification and evaluate equivalency of a foreign educated pharmacy graduate is the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Examination Committee (FPGEC) of the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy.
(2) Under Subsection 58-17b-304(6), an applicant for a pharmacy intern license shall:
(a) be a current pharmacy student in a college of pharmacy accredited by the ACPE, as evidenced by written verification from a dean of the college;
(b) hold a graduate degree from a foreign pharmacy school and have received a certificate of equivalency from an approved credentialing agency under Subsection (1); or
(c) have been accepted to a college of pharmacy accredited by the ACPE, as evidenced by a written acceptance letter from the college of pharmacy showing that the applicant is expected to begin coursework in the college of pharmacy no more than 90 days from the date of the application.
(3) Under Subsection 58-17b-305(1)(e), a pharmacy technician shall complete a training program that:
(a) is accredited by:
(i) ASHP; or
(ii) the Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools (ABHES); or
(b) is conducted by:
(i) a program approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board; or
(ii) a branch of the Armed Forces of the United States; and
(c) meets the following standards:
(i) requires completion, while licensed as a pharmacy technician trainee, of at least 180 hours of directly supervised practical training in a licensed pharmacy by a licensed pharmacist in good standing; and
(ii) has written protocols and guidelines for the teaching pharmacist outlining the use and supervision of pharmacy technician trainees that address:
(A) the specific manner in which supervision will be completed; and
(B) an evaluative procedure to verify the accuracy and completeness of any act, task, and function performed by the pharmacy technician trainee.
(4) A pharmacy technician trainee shall complete a pharmacy technician training program and pass the required examination in Subsection R156-17b-303c(4) within two years after obtaining their pharmacy technician trainee license, unless otherwise approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board for good cause showing exceptional circumstances. An individual who fails to comply with this time frame shall repeat a pharmacy technician training program in its entirety if the individual pursues licensure as a pharmacy technician.
(5)(a) A Division approved program or program in ASHP candidate status shall notify a student before enrollment that if the program is denied accreditation status while the student is enrolled in the program, the student will be required to complete education in another program with no assurance of how many credits will transfer to the new program.
(b) A Division approved program or program in ASHP candidate status that is denied accreditation shall immediately notify the Division, enrolled students, and student practice sites, of the denial.
(c) The notice required in Subsection (5)(b) shall instruct each student and practice site that:(i) the program no longer satisfies the pharmacy technician license education requirement in Utah; and(ii) enrollment in a different program meeting requirements in Subsection R156-17b-303a(3) is necessary for the student to complete training and to satisfy the pharmacy technician license education requirement in Utah.
(6) An applicant from another jurisdiction seeking licensure as a pharmacy technician in Utah who does not meet the qualifications for licensure by endorsement in Subsection 58-1-302(2), meets the qualifications for licensure in Subsections 58-1-302(3), 58-17b-305(1)(e), and 58-17b-305(1)(f) if the applicant:
(a)(i) has engaged in the practice of a pharmacy technician for a minimum of 1,000 hours in that jurisdiction within the past two years; or
(ii) has equivalent experience as approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board; and
(b) has current PTCB or ExCPT certification.” “R156-17b-302. Licensure – Examinations. is now R156-17b-303c. Change to the following verbiage:
R156-17b-303c. Qualifications for Licensure – Pharmacist and Pharmacy Technician – Examinations.
(1) An applicant seeking licensure as a pharmacist under Subsection 58-17b-303(1), shall pass the following examinations within five years of graduation from a pharmacy program described in Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(e):
(a) the NAPLEX with a passing score established by NABP; and
(b) the Utah MPJE with a passing score established by NABP.
(2) An applicant seeking licensure as a pharmacist by endorsement under Subsection 58-17b-303(3), shall pass the Utah MPJE, with a passing score established by NABP.
(3) An applicant under Subsection 58-17b-303(1) or Subsection 58-17b-303(3) who has failed a required examination three times and wishes to retake the exam shall:
(a) meet with the Board to request authorization to test up to two additional attempts; and
(b) complete any additional training the Board may require before any approved additional attempts.
(4) An applicant under Subsection 58-17b-303(1) or Subsection 58-17b-303(3) who has failed a required examination five times and who wishes to retake the exam shall complete another education program in accordance with Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(e) before an additional authorization to test.
(5) An applicant shall pass any required examination within five years of graduation from an education program in accordance with Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(e).
(6)(a) Under Subsection 58-17b-305(1)(f), an applicant for licensure as a pharmacy technician shall pass the PTCB or ExCPT with a passing score established by the certifying body.(b) A PTCB or ExCPT certificate shall show a valid date and that the certification is active.
(7) In addition to any applicable examination requirements of Subsection 58-17b-303(1)(g) or Subsection 58-17b-303(3)(i), a graduate of a foreign pharmacy school seeking licensure under Subsection 58-17b-303(2) shall obtain a passing score on the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Examination Committee (FPGEC) examination.
R156-17b-309. Continuing Education.
Under Section 58-17b-310 and Subsections 58-1-203(1)(g) and 58-1-308(3)(b), this section establishes the continuing education (CE) requirements for renewal or reinstatement of a pharmacist or pharmacy technician license for each two-year renewal cycle.
(1) A pharmacist shall complete at least 30 CE hours which shall:
(a) include 12 hours of live or technology-enabled participation in lectures, seminars, or workshops;
(b) be relevant to the licensee’s professional practice;
(c) include one hour of pharmacy law or ethics;
(d) if engaging in the administration of vaccines under Section R156-17b-621, include two hours in vaccine-related topics;
(e) if engaging in the administration of prescription drugs or devices under Section R156-17b-621 or R156-17b-625, include two hours in topics related to the administration of those prescription drugs or devices; and
(f) if dispensing a self-administered hormonal contraceptive in accordance with Title 26B, Chapter 4, Family Planning Access Act under Section R156-17b-621b, include two hours in topics related to hormonal contraceptive therapy.(2)(a) A pharmacy technician shall complete at least 20 CE hours, which shall include:(i) six hours of live or technology-enabled participation at lectures, seminars, or workshops;(ii) one hour of pharmacy law or ethics; and(iii) if engaging in the administration of vaccines under Section R156-17b-621, two hours in vaccine-related topics.(b) Current PTCB or ExCPT certification shall fulfill each CE requirements for a pharmacy technician, except for vaccine-related topic hours that may be required under Subsection (2)(a)(iii).(3)(a) If a licensee first becomes licensed during the two-year renewal cycle, the licensee’s required number of CE hours shall be decreased proportionately according to the date of licensure.(b) The Division may defer or waive each CE requirements as provided in Section R156-1-308d.(4) CE credit shall be recognized as follows:(a)(i) one live CE hour for attending one Board of Pharmacy meeting, up to a maximum of two CE hours during each two-year period; and(ii) these hours may count as “”pharmacy law or ethics”” hours;(b)(i) two CE hours for each hour of lecturing or instructing a CE course or teaching in the licensee’s profession, up to a maximum of ten CE hours during each two-year period;(ii) the licensee shall document the course’s content and intended audience such as pharmacists, pharmacy technicians, pharmacy interns, physicians, or nurses; and(iii) public service programs, such as presentations to schoolchildren or service clubs, are not eligible for CE credit; and(c) CE credit shall be approved by, conducted by, or under the sponsorship of one of the following:(i) institutes, seminars, lectures, conferences, workshops, various forms of mediated instruction, and programmed learning courses, presented by an ACPE-approved institution, individual, organization, association, corporation, or agency;(ii) programs approved by health-related CE approval organizations, if the CE is nationally recognized by a healthcare accrediting agency and is related to the practice of pharmacy;(iii) Division training or educational presentations;(iv) educational meetings that are ACPE accredited and are sponsored by the Utah Pharmacy Association, the Utah Society of Health-System Pharmacists, or other professional organization or association; or(v) for pharmacists, programs of certification by qualified individuals such as certified diabetes educator credentials, board certification, or other certification as approved by the Division in collaboration with the Board.(5) A licensee shall maintain documentation sufficient to prove compliance with this section, for a period of four years after the end of the renewal cycle for which the CE is due, by:(a) maintaining registration with the NABP e-Profile CPE Monitor plan or the NABP CPE Monitor Plus plan; and(b) maintaining a certificate of completion or other adequate documentation for CE that cannot be tracked by the licensee’s NABP plan.
The data contained in this 2012 Annual Scorecard are accurate as of December 2012 . Because statutes and regulations are continually revised, the data are subject to change. These data have been verified with the state board of pharmacy. This scorecard is updated on an annual basis in order to incorporate statutory and regulatory changes. A new scorecard will be issued in July 2013.
Scoring rationale for Education and Training:
In order to protect the public and help ensure patient safety, it is important that pharmacy technicians are properly educated and trained. The most rigorous training is accredited training. The sole entity empowered to accredit pharmacy-technician training programs is the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP). Please note that this is “programmatic accreditation” – not “institutional accreditation.” It is the content of the training program – as measured against established standards – that is being evaluated and accredited. Accredited training is vital to protecting patient safety because it means that a pharmacy-technician training program has met established quality standards to provide assurance and confidence to the public. For more information, please see http://www.ashp.org/menu/Accreditation/TechnicianAccreditation.aspx.
Scoring rationale for Certification:
Certification is the process by which a nongovernmental agency or association grants recognition to an individual who has met certain predetermined qualifications specified by that agency or association. This is often determined by an examination process. Numerous organizations have recommended that the certification exam conducted by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB) should be recognized as the sole, nationally-accredited certification exam for pharmacy technician certification – including the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy (NABP), the Texas State Board of Pharmacy (TSBP), and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). In a recent report, NABP recommended that states be encouraged to “recognize certification by the Pharmacy Technician Certification Board (PTCB).” Moreover, NABP performed a psychometric audit of the PTCB’s pharmacy technician certification examination (PTCE) in 2001 and determined that the PTCE is psychometrically sound, defensible, and valid. In May 2010, the TSBP awarded the PTCB with the Pharmacy Technician Certification Provider contract in Texas. PTCB was selected for the contract after a rigorous bidding and evaluation process that included formal reviews and evaluations from three independent psychometricians. TSBP confidently recognizes PTCB as the single provider of certification examinations for pharmacy technicians. In addition, in June 2010, the VA began requiring PTCB certification for VA pharmacy technicians employed at grade GS-6 and above.
Scoring rationale for Registration/Licensure:
Registration/licensure is the process by which the state maintains a list of all pharmacy technicians in the state and grants permission for an individual to work as a pharmacy technician in the state based on the applicant’s completion of all pre-requisites to registration/licensure – such as required training and certification.
Scoring rationale for Continuing Education:
Continuing education enables pharmacy technicians to fulfill their professional responsibility to maintain competence and up-to-date knowledge and skills in an environment of technological advances and increasingly complex, new medications and therapies.
Our Mission
The Emily Jerry Foundation is determined to help make our nation’s, world renowned, medical facilities safer for everyone, beginning with our babies and children. We are accomplishing this very important objective by focusing on increasing public awareness of key patient safety related issues and identifying technology and best practices that are proven to minimize the “human error” component of medicine. Through our ongoing efforts The Emily Jerry Foundation is working hard to save lives every day.
Recent Posts
Archives
Recent News
Happy Heavenly 22nd Birthday Emily + Upcoming Pacific Coast Patient Safety Conference
February 24, 2026
By ejfadmin
Tomorrow, I’m really looking forward to heading to Monterey, California to speak on behalf of the Emily Jerry Foundation at the Pacific Coast Patient Safety Conference, hosted by the California Society of Health – System Pharmacists. But today… Read More
Dean’s Hour Recap at Touro College of Pharmacy
February 9, 2026
By ejfadmin
The week before last truly meant a great deal to me. I was honored to be invited back to Touro College of Pharmacy to deliver another Dean’s Hour lecture, after having the privilege of speaking there last April…. Read More
Speaking Engagements at Touro University’s College of Pharmacy Hosted by the NYC Chapter of the New York State Council of Health-System Pharmacists
January 23, 2026
By ejfadmin
I’m really looking forward to heading to New York City this morning for two very meaningful speaking engagements at Touro University’s College of Pharmacy. This journey began with an invitation to deliver a CE presentation at the NYCSHP… Read More